Table of contents
- Understanding Cloud Workloads
- Why is Cloud Workload Protection Important?
- Benefits of CWPP
- Core Components of Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
- How Cloud Workload Protection Works
- Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Workload Protection
- Choosing the Right Cloud Workload Protection Solution
- Why a Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is not enough
- Introducing CNAPP: A Unified Defense System
- Benefits of a CNAPP
- About the Orca Security Cloud Security Platform
- Cloud Workload Protection FAQs
The evolution of cloud computing began as early as the mid-20th century, with the dominance of mainframe computers. Utility computing emerged in the early 2000s, followed by virtualization technology in the mid-2000s. All these technologies paved the way for agile and scalable cloud computing as we know it today, and adoption quickly grew. However, security concerns appeared due to the shared nature of cloud resources, shadow IT, potential vulnerabilities, and the dynamic nature of cloud environments. In response, Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) were introduced to help organizations manage the workloads they run in the cloud and protect them from risks.
A Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is a cybersecurity solution that focuses on securing cloud-based workloads across virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions by providing continuous threat and monitoring protections. Continue reading this article as we explore the ins and outs of CWPP.
Understanding Cloud Workloads
The magic of cloud computing boils down to something called a cloud workload. A cloud workload is the engine that powers cloud applications and services. Simply put, a cloud workload is a collection of resources, applications, processes, and tasks needed to run anything from a simple application to a complex service. It may include things like computing power, storage, networking, applications themselves, and data processing tasks.
The beauty of cloud computing is its versatility in delivering these workloads. For instance, cloud workloads come in different types and can be delivered in various ways, depending on your needs:
- Virtual machines (VMs): Imagine these as super-efficient servers that allow multiple operating systems to run on a single physical host, offering you flexibility and control.
- Containers: Containers provide a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications while providing isolation between applications and their dependencies, allowing them to run consistently across different environments.
- Serverless: Serverless computing allows developers to write and deploy code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
While cloud computing offers many benefits, workloads are vulnerable to various risks:
- Data breaches and loss: A data breach occurs when there is unauthorized access to data as a result of weak authentication, misconfigured access control, malware, vulnerability, or insider threats.
- Compliance and legal risks: Since data privacy is a growing concern, storing data in the cloud subjects organizations to various regulatory requirements regarding data protection, privacy, and residency.
- Service outages and downtime: Infrastructure failures and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can overwhelm the resources available hence leading to service interruptions, slowdowns, or outages for legitimate users.
Why is Cloud Workload Protection Important?
According to the Orca Security 2025 State of Cloud Security Report, nearly a third of cloud assets are in a neglected state, leaving them more susceptible to compromise from attackers. More troubling, 89% of organizations have a neglected asset that is accessible from the Internet.. These publicly exposed assets are prime targets for threat actors.
Cloud workload protection plays a crucial role in protecting against threats in cloud environments by providing continuous monitoring of cloud workloads, identifying vulnerabilities, detecting malware, and helping organizations implement data protection measures.
Benefits of CWPP
Once implemented, Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs) provide organizations with significant benefits, including:
- Visibility: CWPP solutions offer visibility into cloud workloads, showing the OS and applications running on the workload, as well as the versions and installed patches.
- Reduced attack surface: CWPP solutions can detect vulnerabilities on cloud workloads, including virtual machines, containers, serverless functions, and applications.
- Advanced threat detection: CWPP solutions use advanced threat detection techniques, including machine learning, signature-based detection, and heuristics-based detection to identify and prevent malware and other security threats.
- Improved compliance: CWPP solutions assist organizations in meeting compliance requirements by securing workloads in the cloud.
Core Components of Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
CWPPs offer a range of features that work together in safeguarding workloads from potential threats. Here is a breakdown of the core components of CWPP:
- Inventory
A CWPP provides a complete inventory of cloud assets, what operating systems and versions they’re running, as well as any installed software packages. In the case of a zero-day outbreak, the inventory can be searched to quickly understand exposure and any critical remediations that are needed.
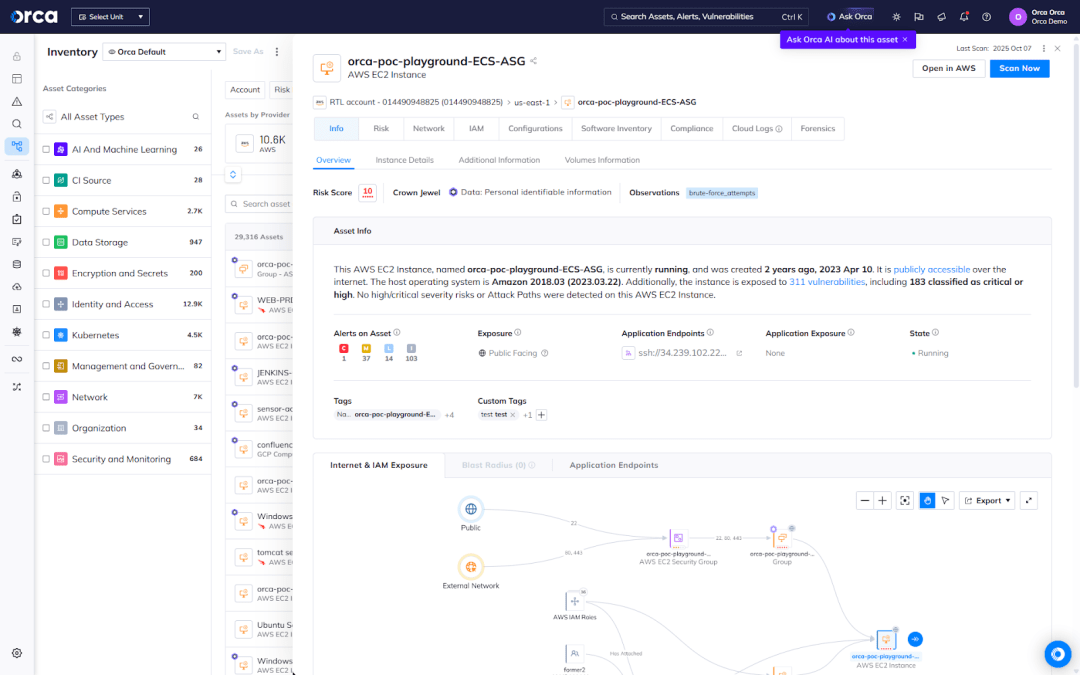
- Continuous monitoring and threat detection
CWPP solutions leverage robust threat detection techniques, such as behavioral analysis, machine learning, signature-based detection, and heuristics-based detection to identify malware and other security threats. - Vulnerability assessment
CWPP solutions offer continuous vulnerability assessment capabilities to identify and prioritize security weaknesses within cloud workloads. - Data protection and encryption
CWPPs prioritize data security by detecting sensitive data in the cloud and ensuring it is properly secured. - Secrets detection
CWPPs check if any secrets are stored insecurely that could enable an attacker to move laterally or access sensitive data.
How Cloud Workload Protection Works
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs) safeguard workloads such as virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions across dynamic cloud environments. While the goal remains the same—to protect workloads from vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and active threats—the methods used to achieve this have diversified. Today, three primary CWPP approaches coexist: traditional agent-based, lightweight sensor-based, and agentless.
Traditional Approach: Heavyweight Agent-Based CWPP
The earliest CWPP solutions relied on installing software agents directly on each workload to collect telemetry and monitor for suspicious activity. This method provided deep visibility but came with significant trade-offs.
- Complex deployment and maintenance: Installing and maintaining agents across large cloud estates is time-consuming and often causes friction between security and DevOps teams.
- Partial coverage: Because agents must be manually deployed, some workloads are inevitably missed, leading to visibility gaps.
- Performance impact: Agents consume CPU and memory resources on every workload, which can affect performance and scalability.
While still in use, this traditional approach often struggles to keep pace with the speed, elasticity, and diversity of modern cloud environments.
Lightweight Sensor-Based CWPP
To overcome the operational burden of legacy agents, modern CWPP vendors have introduced lightweight sensors. These are designed to deliver real-time visibility and detection without the heavy footprint or management complexity of traditional agents.
- Built for modern environments: Sensors integrate seamlessly into containerized, virtualized, and hybrid infrastructures.
- Efficient operation: Using technologies such as eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter), sensors observe workload behavior with minimal resource impact.
- Real-time protection: They enable immediate detection of active threats, policy violations, and anomalous activity.
For example, Orca Sensor is a lightweight eBPF-based technology that delivers runtime visibility
and protection for advanced Cloud Detection and Response (CDR).
While this type of visibility provides advantages, especially for sensitive workloads, it doesn’t provide the full workload coverage that organizations need to maintain a strong security posture. That brings us to the next approach: agentless CWPP.
Agentless CWPP
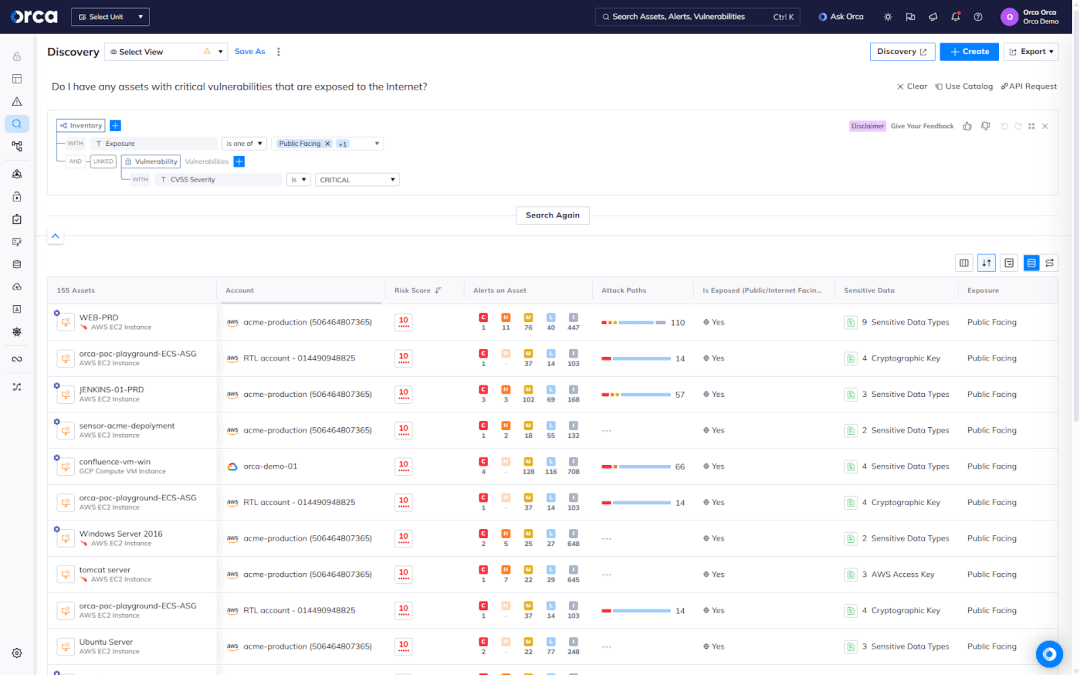
Agentless CWPP solutions provide workload visibility without installing software on the workloads themselves. Instead, like other agentless cloud security solutions, they integrate directly with cloud provider APIs to collect data, scan for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, and assess overall risk.
- Fast, frictionless deployment: Provides full visibility across all workloads and accounts within minutes, including new assets as they appear.
- Zero performance impact: Because no software runs inside workloads, there is no CPU or memory overhead.
- Centralized management: Security teams can manage protection uniformly across all environments without worrying about agents or sensors.
Agentless CWPP has become a cornerstone of modern cloud security, offering comprehensive visibility, scalable deployment, and low operational overhead. Many organizations start here to establish cloud hygiene and risk prioritization, and then selectively augment with sensors where runtime detection is critical.
Are all agentless CWPP platforms equal?
Not exactly. While many security vendors now offer agentless capabilities, the depth and scope of these implementations can vary widely. Some vendors that originally relied on agent-based architectures have since added agentless features to meet market demand. In these cases, the agentless functionality is often limited to specific use cases—such as vulnerability scanning or configuration assessment—and may still depend on agents for deeper workload visibility or runtime data.
Other platforms were designed to operate agentlessly from the start, allowing them to gather a broader range of information without installing software inside workloads. These solutions typically integrate directly with cloud provider APIs or storage layers to perform scans, assess risk, and provide contextual insights while minimizing operational overhead.
The Orca Cloud Security Platform follows this agentless-first design. Its patented SideScanning™ technology collects data from the workloads’ runtime block storage and reconstructs their file systems—including operating systems, applications, and data—in a secure, read-only view. This approach enables comprehensive risk analysis with no impact on workload performance and provides continuous visibility across the cloud environment.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Workload Protection
Here are some of the best practices to implement with your CWPP:
1. Conduct a cloud security assessment
Conducting a cloud security assessment involves evaluating the security status of your cloud environment to identify potential risks, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement. This also helps you prioritize security measures and focus your efforts where they’re most needed.
2. Secure sensitive workloads
After establishing broad visibility through your CWPP, implement real-time security for sensitive workloads to provide additional protection against active threats. Lightweight, sensor-based runtime protection can help detect and respond to suspicious activity as it occurs, offering deeper visibility into workloads that process or store critical data. Examples include virtual machines that expose secrets or storage buckets containing sensitive information.
3. Adopt the principle of least privilege (PoLP)
PoLP is a fundamental security principle that advocates granting users and systems only the minimum level of access or permissions necessary to perform their tasks. By adopting PoLP, organizations can reduce their attack surface, enhance access control mechanisms, and improve overall security posture within their cloud environment.
4. Continuously monitor and automate security policies
Continuous monitoring keeps a watchful eye on your cloud environments. CWPPs perform automated security screening, such as vulnerability scanning and patch management to improve efficiency and reduce response times.
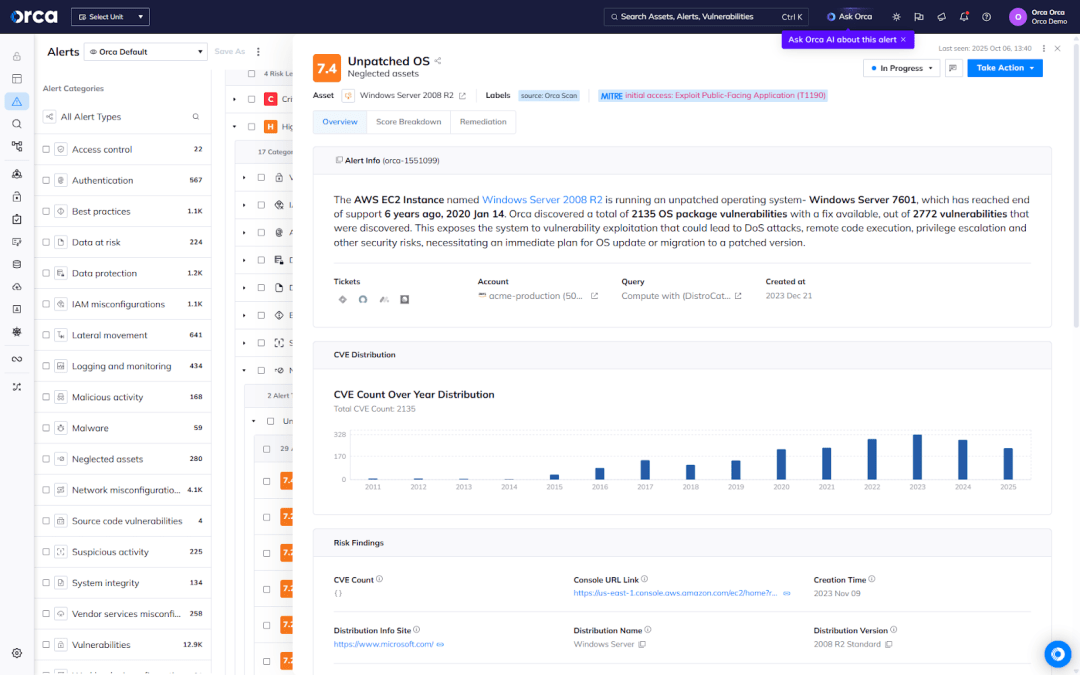
5. Regularly update and patch cloud workloads
It’s important to regularly update operating systems and applications running on cloud workloads to prevent vulnerabilities. If vulnerabilities are detected by the CWPP, security teams need to quickly be able to understand which risks are the most critical so these can be fixed first. A CWPP can help prioritize risks by applying risk scores based on context and risk severity.
6. Provide training and awareness in cloud security
Providing comprehensive training and awareness programs for your cloud users is key. By educating employees, developers, and IT personnel about cloud security best practices, policies, and procedures, many issues can be prevented.
Choosing the Right Cloud Workload Protection Solution
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) are your guardians in the cloud, but with so many options, picking the right one can be tough. Here are 4 recommendations to guide you:
1. Understand the key features to look for in a CWPP solution
Different CWPPs offer varying capabilities so it’s important to ensure the below key features are included:
- Robust vulnerability scanning and assessment capabilities to identify security weaknesses, misconfigurations, and known vulnerabilities within cloud workloads.
- Advanced malware detection mechanisms, such as behavioral analysis, machine learning, and heuristics based detection in addition to signature based.
- Features for secure configuration management, compliance monitoring, and policy enforcement to ensure cloud workloads adhere to security best practices and regulatory requirements.
- Incident response and remediation capabilities, including alerting, incident investigation, automated response actions, and integration with security orchestration and automation platforms.
- A centralized management console or dashboard that provides comprehensive visibility, policy management, and reporting capabilities across cloud workloads, facilitating efficient security operations and compliance management.
- Technology that supports both agentless visibility and real-time protection, with these capabilities fully integrated within a single, unified view to simplify operations and provide consistent risk context across all workloads.
2. Consider multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud environments
If you operate in a multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud environment, vendor lock-in can be a concern. You can tell whether a CWPP solution is fit for your estate by considering the following factors:
- Ensure that the chosen CWPP solution integrates and works seamlessly with the various cloud platforms used by the organization.
- Look for a CWPP solution that provides centralized management and visibility across all cloud platforms. A unified management console enables administrators to monitor security events, enforce policies, and generate reports from a single interface, simplifying security operations in a multi-cloud environment.
- Establish consistent security policies and configurations across all cloud environments to maintain a unified security posture.
- Consider data sovereignty regulations and compliance requirements when deploying CWPP solutions in multi-cloud environments.
- Implement resilience and redundancy strategies to ensure continuous protection and availability of security controls in multi-cloud environments.
3. Why AI-driven CWPP is something you should look for
To reduce operational burden and accelerate remediation, AI-driven capabilities in Cloud Workload Protection Platforms can deliver several benefits:
- Quickly detect sophisticated and evolving threats that traditional security approaches may miss.
- Automate incident response and remediation processes, allowing organizations to respond to security threats faster.
- Enhance visibility into cloud workloads and security events by analyzing vast amounts of data generated by cloud environments.
- Simplify and accelerate cloud workload investigations so teams can for instance quickly understand exposure to zero-day risks.
4. Evaluate vendors and products
Once you understand your needs and key features, it’s time to evaluate vendors and products. Here are some tips:
- Read reviews and case studies: See how other companies have used CWPPs to address their security challenges.
- Request demo and POC: Experience the platform firsthand and see if it fits your workflow.
- Consider cost and support: Compare pricing models and evaluate the level of customer support offered.
Why a Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is not enough
While Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) are essential to cloud security, they are only a small part of the cloud security puzzle. CWPPs only cover cloud workloads and lack visibility into the cloud control plane, such as misconfigurations and overly permissive identities.
This limited visibility impacts the tool’s ability to provide full security coverage and effective alert prioritization. Any risks due to cloud misconfiguration (such as MFA not being enabled for the ‘root’ user account or KMS encryption keys not being rotated) cannot be detected by a CWPP.
Historically, many organizations addressed these gaps by deploying multiple standalone tools, such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM), API Security, and Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) solutions. While these tools helped extend coverage, they also introduced operational complexity and redundant alerting.
Over time, the limitations of this fragmented approach gave rise to Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs), which unify these capabilities under a single framework. Today, most organizations are modernizing their cloud security by adopting CNAPPs that include CWPP functionality as a core component. This shift reflects a growing emphasis on holistic visibility, contextual risk prioritization, and simplified operations.
Introducing CNAPP: A Unified Defense System
A Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) provides end-to-end security across cloud-native applications, workloads, and infrastructure. Rather than relying on separate point solutions, CNAPPs deliver comprehensive protection through a single, integrated platform.
Several factors have driven the adoption of CNAPPs:
- Reduced complexity: As organizations operate across multiple cloud providers, consolidating multiple security tools into one CNAPP helps simplifyoperations, reduce tool sprawl, and streamline security workflows.
- Unified visibility and control: CNAPPs provide a centralized view of security posture across workloads, configurations, identities, and data, enabling teams to understand not just isolated risks but also how they interconnect to form potential attack paths.
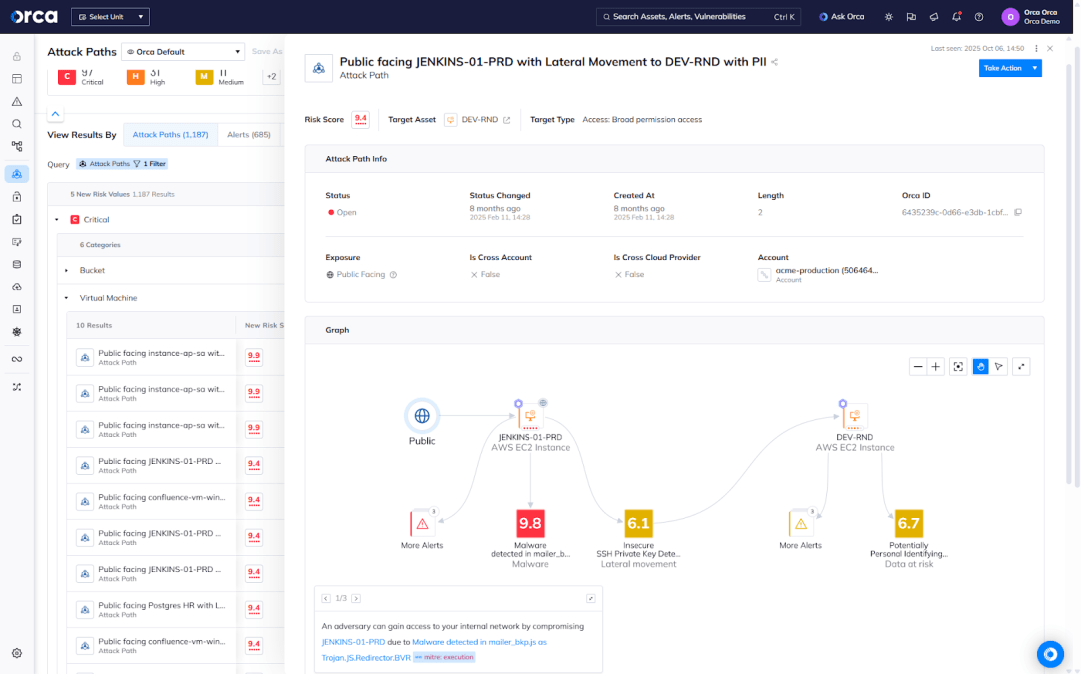
- Improved integration and orchestration: CNAPPs facilitate seamless integration into existing workflows, allowing organizations to automate risks for remediation, orchestrate responses to security events, and enforce consistent policies across diverse cloud-native environments.
- Enhanced threat detection and response: By combining many different capabilities into one platform, CNAPPs can apply advanced AI, machine learning, and behavioral analytics to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
- Scalability and flexibility: Modern CNAPPs scale seamlessly with cloud growth and automatically adapt to changes in workloads.
Benefits of a CNAPP
CNAPPs offer several benefits for organizations operating in cloud-native environments. Those benefits include:
- Simplified security management and operations: CNAPPs streamline security management by providing a single platform for monitoring, managing, and enforcing security policies across cloud-native applications, workloads, and infrastructure.
- Collaborative approach: Different stakeholders, such as security and risk management teams, DevOps, DevSecOps, IAM, and IT professionals, can collaborate and implement an integrated security approach using CNAPPs.
- Unified visibility and control: CNAPPs offer unified visibility into the security posture of cloud-native environments, providing a single pane of glass for monitoring security events, vulnerabilities, and compliance status.
- Integrated security capabilities: CNAPPs integrate a wide range of security capabilities, including vulnerability management, malware detection, identity management, misconfiguration detection, compliance checks, API security, data protection, and more into a single platform.
- Shift left security: CNAPPs enable automated security checks by integrating with cloud-native orchestration tools, DevOps and DevSecOps pipelines, and CI/CD workflows. This allows organizations to automate security processes, such as vulnerability scanning, configuration management, and incident response, and embed security into the development lifecycle.
About the Orca Security Cloud Security Platform
The Orca Cloud Security Platform offers a true agentless-first CNAPP that identifies, prioritizes, and remediates security risks and compliance issues for AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Kubernetes, Alibaba Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
Orca’s solution consolidates cloud configuration, workload, identity & entitlement security, multi-cloud compliance, vulnerability management, and more in a single platform. Leveraging a Unified Data Model, Orca contextualizes risks and recognizes when seemingly unrelated issues can create dangerous attack paths. This enables Orca to prioritize risks effectively, reduce alert fatigue, and ensure your teams can focus on the most critical and important tasks.
After a quick setup (usually less than 30 mins), Orca provides deep and wide visibility into all cloud assets and helps organizations continually improve their cloud security posture. Schedule a demo with one of our experts to see how the Orca Cloud Security Platform can uplevel your cloud security.
Cloud Workload Protection FAQs
What’s the difference between CWPP and CSPM?
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) solutions focus on safeguarding workloads, applications, and data within cloud environments, offering tailored security controls such as vulnerability assessment, threat detection, and data protection. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM ) solutions focus on the cloud provider by assessing and managing the overall security posture of the entire cloud environment, evaluating configurations, compliance, and risk exposure across accounts, services, and resources.
Can CWPP be used across different cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)?
In IaaS environments, CWPP solutions secure individual workloads, applications, and data by offering security controls. For PaaS, CWPP ensures application security and data protection, safeguarding against unauthorized access and vulnerabilities. In SaaS environments, CWPP solutions enforce access controls and monitor user activity to protect sensitive data, allowing organizations to maintain security and compliance.
How does Cloud Workload Protection impact system performance?
Deployment methods, such as agent-based or agentless, affect resource usage differently; agents may offer granular visibility but consume CPU and memory resources which can cause performance degradation, whereas agentless approaches have zero impact on performance.
How does a CWPP integrate with existing security tools and workflows?
Most CWPP solutions enable seamless integration with security tools, orchestration platforms, and management systems. CWPP solutions can integrate with event and log aggregation platforms (SIEM), Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools, ticketing platforms, notification systems, and more.
What’s the difference between CWPP and CNAPP?
CWPP solutions were created to protect individual workloads, applications, and data within cloud environments. CNAPP solutions offer CWPP capabilities, but cover much more, including CSPM, CIEM, DSPM, API security and more, and are specifically designed to secure cloud-native applications, microservices, and containerized workloads deployed in cloud environments.
Does the Orca Security CNAPP include CWPP?
Yes, the Orca Platform incorporates cloud workload protection to discover risks in all cloud workloads (VMs, containers, and serverless) such as vulnerabilities, malware, and data at risk. Unlike other CWPPs, Orca is completely agentless, fully deploys in minutes with 100% coverage, and includes wide and deep visibility into risks across every layer of your cloud estate, including cloud configurations as well as workloads.
Table of contents
- Understanding Cloud Workloads
- Why is Cloud Workload Protection Important?
- Benefits of CWPP
- Core Components of Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
- How Cloud Workload Protection Works
- Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Workload Protection
- Choosing the Right Cloud Workload Protection Solution
- Why a Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is not enough
- Introducing CNAPP: A Unified Defense System
- Benefits of a CNAPP
- About the Orca Security Cloud Security Platform
- Cloud Workload Protection FAQs




