Table of contents
Key Takeaways
- Challenge: Protecting cloud native applications required a fragmented tech stack without any purpose-built security tools.
- Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) provide a purpose-built solution to building and protecting cloud native applications from pre-production to runtime and real time security.
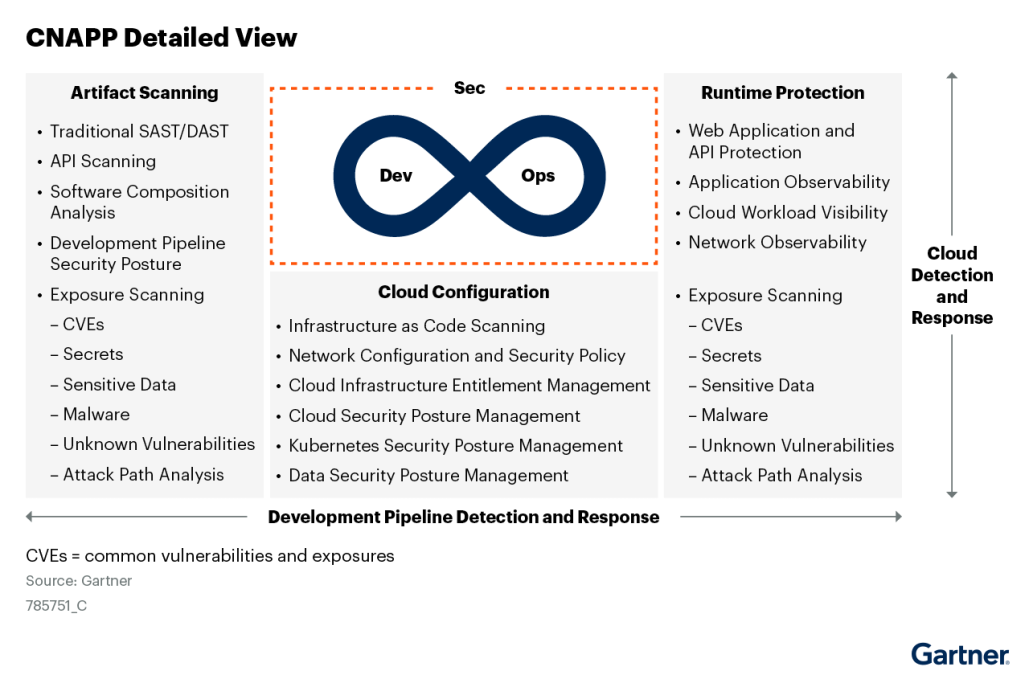
- CNAPP solutions serve as a central platform to deliver a fully integrated experience across capabilities like cloud security posture management (CSPM), cloud workload protection (CWPP), container and Kubernetes security (KSPM), cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM), infrastructure-as-code (IaC) scanning, cloud detection and response (CDR), and vulnerability scanning.
- Agentless CNAPP solutions like Orca deliver a depth of visibility into security risks and compliance across your entire cloud estate—in minutes.
Introduction
In recent years, we have witnessed various advancements within the tech industry, especially with the advent of cloud computing. We have seen businesses rapidly adopting cloud-native application development techniques as they migrate their operations from on-premises and hybrid data centers to the cloud. Consequently, this has brought significant benefits to businesses, driving innovation and growth in their operations, empowered by the scalability and flexibility of the cloud.
However, with this rising popularity of cloud-native applications comes a new set of complexity-related challenges especially in ensuring security across distributed cloud systems. With the increased speed and agility of cloud native development, modern organizations need security controls to be applied much earlier in the software development lifecycle, rather than just in production. In addition, security teams are increasingly reliant on developers and DevOps teams to fix issues in underlying code that is used to deploy Infrastructure as Code and containers. Traditional security tools fall short in these ephemeral environments, which created the need for a comprehensive cloud-native security tool.
Enter the cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP). CNAPP is a modern cloud security solution designed to safeguard cloud-native applications and deliver integrated security across the full cloud-native stack, from infrastructure to applications and data. It combines capabilities like cloud security posture management, workload protection, cloud infrastructure entitlement management, runtime container security, API security, and more—all delivered from a single platform. As cloud-native adoption accelerates, CNAPPs provide the visibility, automation, and protection required in these new cloud environments. Read on to learn what makes CNAPP such an essential solution for your organization.
What is CNAPP? (CNAPP Defined)
Gartner defines a Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) as a “unified and tightly integrated set of security and compliance capabilities designed to secure and protect cloud-native applications across development and production.”
This definition highlights two key aspects of CNAPP:
- Uses a unified platform: CNAPP consolidates a large number of previously siloed security functionalities into a single platform. These functionalities can include:
- Container and Kubernetes Scanning: Identifying vulnerabilities within containerized applications.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Providing an overall view of the security posture of the cloud environment and identifying misconfigurations.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Scanning: Detecting security vulnerabilities within infrastructure code before deployment.
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM): Monitoring and managing user access and permissions in the cloud.
- Cloud Workload Protection (CWPP): Protecting workloads running in the cloud from threats and malware at runtime.
- Vulnerability/Configuration Scanning: Continuously scanning cloud workloads for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations during operation.
- Built for modern cloud-native applications: CNAPP serves as a comprehensive security solution built specifically for modern cloud environments and the applications that run in them. It is specifically designed to address the security challenges of cloud-native applications, which are built with microservices architecture, containers, and orchestration. This provides organizations with a more holistic approach to security throughout the application lifecycle, from development to deployment and runtime.
Understanding Cloud-Native Applications
Cloud-native applications are designed specifically to run on the cloud, leveraging its scalability and flexibility advantages. Here are some of the characteristics of cloud-native applications:
- Modular design: Cloud-native apps are built using microservices architecture, breaking down functionality into smaller, independent services. This allows for faster development, deployment, and scaling.
- Containerized deployment: Cloud-native apps are packaged using containerization technologies such as Docker, and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes for consistent execution across environments.
- Dynamic scaling: Cloud-native apps are highly dynamic with components that scale up and down automatically, optimizing resource utilization.
- API-driven integration: Cloud-native apps rely on APIs to enable seamless communication and integration between other cloud-native apps, cloud services, or data storage.
- Decentralized data storage: Data in cloud-native apps is often stored across distributed cloud storage resources, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
While powerful, these features also create unique security challenges. Traditional tools struggle to keep up with these highly dynamic apps. That’s where Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) come in. They’re designed specifically to address the security needs of cloud-native apps.
The Emergence of CNAPP
As more and more companies adopt the cloud, the need for cloud-native security has become evident. Traditional security solutions dealt with the initial cloud security demand by ‘lifting and shifting’ agent-based security solutions to the cloud. However, it quickly became clear that these solutions that relied on agents being deployed on every asset could only provide coverage of up to 50-70% of cloud resources, leaving dangerous blind spots. In addition, separate point solutions were being introduced for each layer of the tech stack (such as CWPP, CSPM, CIEM) and application development stage, which provided poor overall visibility, created high overhead and required tedious manual correlation. CNAPP solutions then emerged, representing a shift towards a more unified and integrated approach to cloud security.
CNAPP solutions differ from traditional security platforms and tools in that they are specifically designed for dynamic cloud environments and the applications that run on them, and consolidate security in a single platform to deliver a holistic approach to cloud security. By consolidating key capabilities into an integrated solution, a platform with unified functionality focused on emerging cloud risks thus offering automated and API-driven security that keeps up with the pace of the ever-evolving cloud. By leveraging automation and integration, CNAPPs enable organizations to adapt to the dynamic and scalable nature of cloud-native applications while reducing the number of point security tools needed.
Key Components of a CNAPP
An effective CNAPP solution offers robust security for cloud-native applications and environments by combining several critical components. These components work together seamlessly, addressing the unique security challenges posed by dynamic and distributed applications. This integrated approach is what makes a CNAPP so powerful, offering seamless and comprehensive security coverage across application, data, and network security within cloud-native environments.
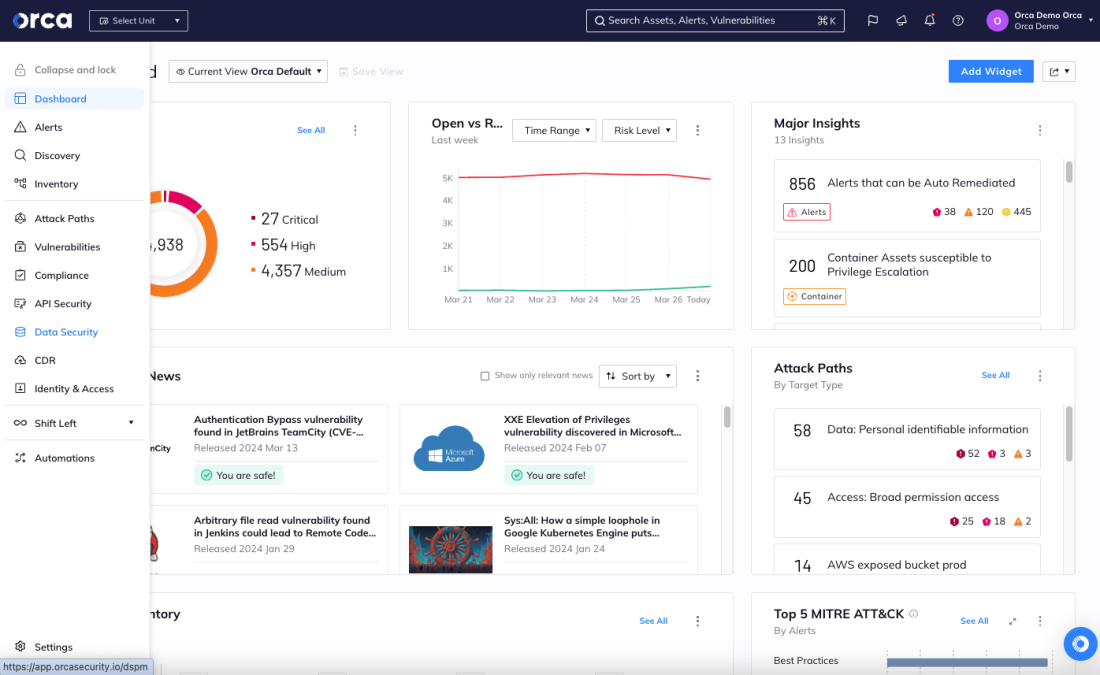
Now, let’s explore the key components that make CNAPP your go-to effective cloud-native security solution:
1. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM manages the overall security posture and compliance status of your cloud environment. CSPM works by continuously monitoring the cloud environment for misconfigurations, security weaknesses, and potential compliance issues. It analyzes cloud resource configurations, identifies deviations from best practices, and helps ensure your cloud environment adheres to security and compliance standards.
CSPM serves as a key CNAPP component as it helps you to proactively identify and remediate security risks before they can be exploited. For example, a CSPM may detect a misconfiguration involving a cloud storage bucket that might have been left publicly accessible and allow security teams to secure the bucket and prevent unauthorized access to the data.
2. Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
Cloud Workload Protection (CWPP) offers deep visibility and risk mitigation for cloud-based resources like VMs, containers, and serverless functions. It provides a detailed inventory of all cloud assets, what OS they are running, which apps are installed, what data they contain – all with detailed version information. CWPPs then continuously monitor these assets for risks such as vulnerabilities, malware, and sensitive data at risk, and enforce security policies to protect your applications and data in the cloud.
3. Cloud Identity and Entitlement Management (CIEM)
CIEM empowers you to manage user access and permissions within your cloud environment with precision. This granular control helps mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. CIEM enforces the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring users only have the access they absolutely need to perform their jobs.
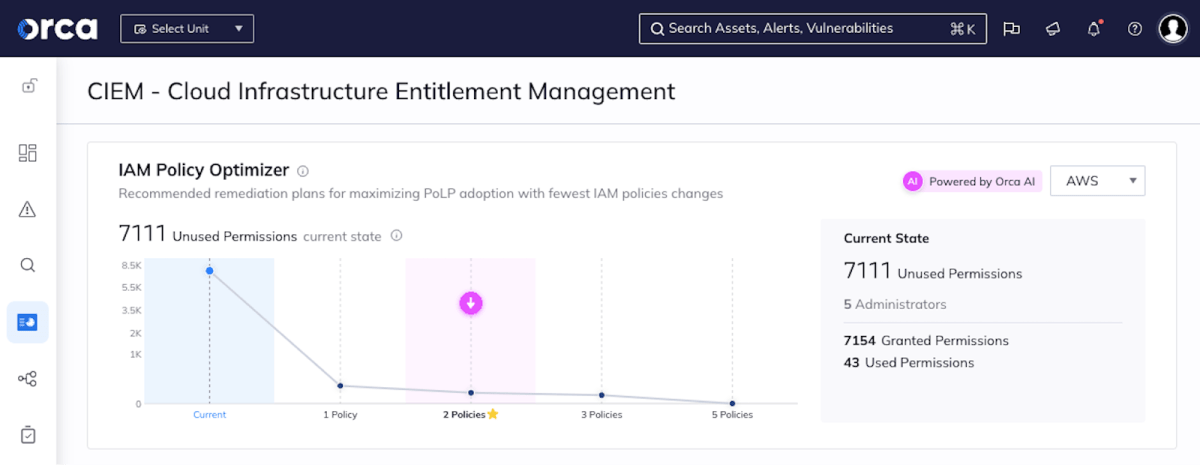
CIEM is a key CNAPP component as it plays a vital role in overseeing entitlements across your cloud-native environments, which can become very complicated, pretty quickly. It can detect potential leaks of sensitive information like secrets or credentials, which could be exploited by attackers to gain access to critical assets.
4. Cloud Detection and Response (CDR)
CDR empowers you to safeguard your cloud environment by continuously monitoring for suspicious activity. This proactive approach enables you to detect, investigate, and respond swiftly to potential security incidents. CDR utilizes a combination of powerful tools and techniques, including log analysis, threat intelligence, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM). By analyzing data from various sources, CDR can identify potential threats and enable rapid response.
CDR is a key CNAPP component because it offers comprehensive visibility across your cloud environment. It can automatically correlate threats from real-time signals, cloud activity, and audit logs. This allows you to track potential attacker movements and take swift action to minimize the impact of incidents. For example, CDR may detect an unusual login attempt from a foreign country targeting a particular user account and flag it as an anomaly, alerting security teams to investigate and prevent a potential breach.
5. Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) security
CI/CD Security seamlessly integrates automated security checks within the development pipeline, ensuring vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the development process. This significantly reduces the risk of inadvertently deploying insecure applications to production.
CI/CD security is a key component of CNAPP because, by definition, CNAPP is concerned about security both in development and production environments. This empowers developers to build secure software from the ground up, fixing any issues earlier in the process when they are far less costly to fix, and significantly reducing the risk of deploying vulnerable applications. This is effectively known as “shifting security left.” For example, a developer may commit code that introduces a known SQL injection vulnerability. Luckily, the CI/CD security scans the code and identifies the vulnerability before it is deployed, allowing the developer to fix the issue before it can be exploited by attackers.
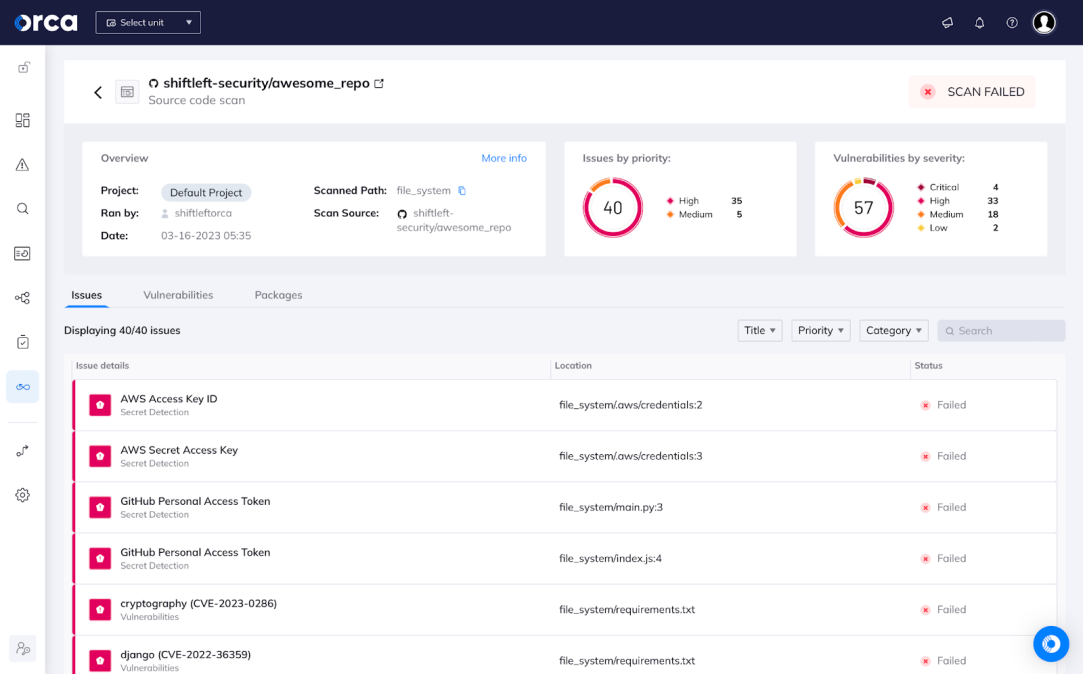
6. Container and Kubernetes security
Container and Kubernetes Security becomes crucial once applications are deployed in cloud-native environments, and protects containerized applications and Kubernetes orchestration platforms by identifying vulnerabilities in container images and enforcing security policies within Kubernetes clusters.
As containerized applications become increasingly popular in cloud-native environments, container and Kubernetes security must serve as a key component of CNAPP to deliver protection for containerized applications and the underlying Kubernetes infrastructure. For example, a CNAPP’s container and Kubernetes security may detect a vulnerability within a container image that could allow attackers to escalate privileges. The CNAPP would then allow teams to isolate the containerized application, preventing attackers from exploiting the vulnerability to gain access to the system.
CNAPP Benefits
Implementing a CNAPP provides organizations with substantial benefits:
- Improved cloud security posture and risk management: A CNAPP gives you greater visibility into risks across your distributed, dynamic cloud infrastructure. This helps you to prioritize vulnerabilities and close security gaps.
- Enhanced visibility across cloud environments and applications: The unified nature of CNAPPs provides visibility across multiple cloud platforms and applications. Using an agentless-first CNAPP ensures full coverage and eliminates blind spots in your security infrastructure.
- Automation of security tasks and compliance checks: CNAPP automation simplifies audits and streamlines compliance checks for regulations such as PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- The ability to adapt to the dynamic and scalable nature of cloud-native applications: CNAPPs are designed and built to handle the scalability and constant changes inherent in cloud-native environments and integrate into the CI/CD process.
- Reduce the number of point security tools needed: A single CNAPP platform replaces the need for multiple disparate security tools. This reduces complexity by providing an integrated solution for end-to-end protection of cloud-native applications. Additionally, organizations can significantly reduce costs by consolidating security tools into a single CNAPP solution because fewer tools mean lower licensing fees, less maintenance, and less operational overhead.
Choosing the right CNAPP for your business
Selecting a CNAPP solution is an important decision that requires careful evaluation of your organization’s needs and priorities. When choosing a CNAPP solution, there are a few key factors to keep in mind:
1. Compatibility
First, ensure the CNAPP integrates well with your existing cloud environment and applications. Whether you are using Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, or a combination, choose a CNAPP built to secure each platform. Some CNAPPs are designed as a single integrated solution across multiple clouds. These can reduce complexity and provide centralized visibility and control. For example, Orca offers cloud compatibility across major cloud service providers such as AWS, GCP, and Azure which enables organizations to proactively secure their cloud-native applications and infrastructure, regardless of the specific cloud service provider they utilize.
In addition, look for the right technical integrations to allow the cloud security process to seamlessly fit into your workflows. For instance, a CNAPP should integrate with repository tools (e.g., DockerHub, JFrog Artifactory), CI/CD tools (e.g., Jenkins, Gitlab CI, GitHub), ticketing systems (e.g., Jira, Azure DevOps, ServiceNow), SIEMs (e.g., Splunk, SumoLogic, AzureSentinel, Datadog), SOARs (e.g., Cortex XSOAR), and notification offerings (e.g., Slack, PagerDuty).
2. Scalability, reliability, and performance
Your CNAPP must be able to handle the scale and performance demands of your cloud-native applications. As your applications and data grow, the CNAPP should scale automatically to meet increased workloads without impacting functionality or speed. When it comes to the reliability of your CNAPP solution, high availability and redundancy should always be prioritized to minimize disruption.
3. Compliance and regulatory requirements
Regulatory compliance is essential for many organizations when it comes to cloud security. You should always ensure that the CNAPP you select simplifies the process of adhering to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOC 2. The CNAPP should provide automated compliance checks, security policy enforcement, and reporting to simplify auditing processes. Some CNAPPs like Orca Security offer customizable, out-of-the box compliance frameworks to make it faster and easier to implement necessary controls.
4. Truly built as a single platform
As obvious as it may sound, one of the most important factors to consider when selecting your CNAPP solution is – whether it actually ‘is’ a CNAPP. Some vendors in the space offer an ‘integrated’ platform but are actually just offering separate products under the same name. These ‘integrated’ products do not share telemetry, and sometimes not even the same administration console. This type of integration does not provide the synergy benefits of a platform that was built as one consolidated solution from the ground up, such as the Orca CNAPP.
“All services should be fully integrated, not loosely coupled independent modules (typically resulting from a vendor’s internal silos, poorly integrated OEM components or those added from an acquisition). Integration should include the front-end console, unified policy across multiple points of inspection and a unified back-end data model.”
2023 Gartner Market Guide for Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs)
Choosing the right CNAPP solution for your organization is key to maximizing the benefits of cloud-native application protection. By assessing your compatibility requirements, scalability needs, compliance priorities, and desired functionality, you can find a CNAPP tailored to your business’s pain points. Solutions like the Orca CNAPP are purpose-built to meet all your business security needs for leveraging cloud-native applications.
How to Implement a CNAPP in Your Organization
Implementing a CNAPP solution is a strategic move to strengthen your cloud security posture. However, integrating any new tool into your existing infrastructure requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to follow when rolling out a CNAPP in your organization:
1. Involve key stakeholders early on
With such important infrastructural changes, you must foster open communication and collaboration between DevOps, security, compliance, and cloud infrastructure teams throughout the processes. Their input and buy-in will be essential in ensuring alignment with existing workflows and security policies, leading to a more successful CNAPP implementation.
2. Address implementation challenges
While implementing a CNAPP offers significant security benefits, it is essential to be prepared for potential challenges. Some common hurdles include resistance to change within different teams, a lack of overall awareness about CNAPPs, and technical complexities associated with integration, although this is largely non-existent for agentless-first CNAPPs such as Orca.
An effective strategy is to provide comprehensive training on the CNAPP solution for both technical and non-technical teams. This training fosters in-house security expertise, empowering your team to effectively manage day-to-day security operations and monitoring tasks using the CNAPP.
Conclusion
Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms are the future of cybersecurity in the cloud. As businesses migrate to cloud-native apps and infrastructure, implementing a robust CNAPP becomes key to managing risk, simplifying cloud security, and protecting your most critical data and systems. As discussed in this blog, the right CNAPP offers a multitude of benefits such as improved end-to-end visibility, security automation, adaptive security, reduced complexity, and a solid and compliant cloud security posture. The journey to cloud-native security doesn’t have to be daunting. By partnering with the right security experts, you can confidently embrace the benefits of CNAPP.
Learn more about the Orca CNAPP
The Orca Cloud Security Platform is a consolidated CNAPP built for developers, DevOps and security practitioners alike, integrates seamlessly into the CI/CD process, and allows businesses to keep up with the agility of modern development teams without slowing them down.
After a quick setup (usually less than 30 mins), Orca provides deep and wide visibility into all cloud assets and helps organizations continually improve their cloud security posture in three steps:
- Detect risks: Orca continuously monitors for all cloud risks, including misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, malware, API risks, compliance risks, exposed sensitive data, AI risks, and over-privileged identities from development to production (and back).
- Prioritize risks: Using the full context of risks, Orca shows which ones are critical and need to be addressed right away – something that siloed or poorly integrated cloud security tools cannot do.
- Remediate risks: Orca enables fast remediation with automated and guided remediation options, including remediation code generated with GenAI.
Schedule a demo with one of our experts to see how the Orca CNAPP platform can uplevel your cloud security.
FAQs
Q: What metrics and KPIs are important for evaluating CNAPP effectiveness?
To evaluate a CNAPP’s impact and effectiveness, you should track these key security metrics and KPIs:
- Reduced incidents: The CNAPP should proactively identify and prevent potential security breaches hence ensuring reduced incidents.
- Faster response: The CNAPP’s performance should demonstrate a faster response time to security incidents, minimizing the potential damage caused by security threats.
- Fewer vulnerabilities: The CNAPP’s effectiveness in identifying and addressing security weaknesses should lead to a decreased number of vulnerabilities and misconfigurations across the cloud estate, including infrastructure and workloads.
- Stronger security posture: An effective CNAPP solution should contribute to the overall improvement of your organization’s security posture based on the industry’s security standards.
Q: What is the difference between CNAPP and CSPM/CWPP?
A CNAPP is a comprehensive cloud security solution that integrates various security functions into a single platform, while both CSPM and CWPP focus on offering single security functionalities. CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) focuses on assessing and managing the configurations of cloud environments, while CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platform) focuses on protecting what is running on the workloads. CNAPP combines the functionalities of CSPM and CWPP, along with other security capabilities, to provide end-to-end security for cloud-native applications.
Q: How does CNAPP support multi-cloud environments?
CNAPPs are designed to support multi-cloud environments by providing comprehensive security coverage across multiple cloud platforms. They offer a unified view and management console that allows you to monitor your entire cloud-native environment including its applications and resources consistently, even across different cloud providers.
Q: Can CNAPP integrate with existing DevOps processes?
Yes, CNAPPs can seamlessly integrate with existing DevOps processes. During the implementation of the CNAPP solution, both the development and operations teams should be involved to ensure that it aligns with each team’s workflow processes and requirements.
Q: How does CNAPP support compliance and regulatory requirements?
CNAPPs support compliance and regulatory requirements by automating security tasks and compliance checks. They offer a set of functionalities that help in assessing and managing the security posture of cloud environments, ensuring that organizations adhere to relevant regulations and meet standards for their cloud infrastructure and workloads. Additionally, CNAPPs also streamline compliance reporting, which remains a pain-point for many organizations.
Q: How do CNAPP solutions address the security of third-party APIs and services integrated into cloud-native applications?
Some CNAPP solutions can identify and mitigate security risks associated with third-party APIs and services integrated into cloud-native applications. They continuously monitor and analyze the behavior of APIs and services, and alert when any API risks are found, so security teams can address issues quickly.






