The ISO 27001 compliance framework helps organizations maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. Beyond the need to stay ahead of compliance audits, ISO 27001 compliance remains highly valuable for organizations with a strong cloud footprint, as it provides security and governance teams with a strong foundation for mitigating risks and improving the overall security posture of cloud-based systems.
This blog post will give an overview of the requirements of the ISO 27001 framework, common compliance challenges, as well as how the Orca Security Platform’s compliance capabilities help organizations meet ISO 27001 requirements in an automated, simplified, and strategic way.
What Is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001, an international information security standard, is defined jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Due to the IEC’s involvement, it is sometimes denoted as ISO/IEC 27001, though both terms refer to the same standard.
Initially published in 2005, ISO 27001 underwent a significant revision in 2013, and there have been subsequent minor revisions as well, most recently in 2022.
ISO 27001 compliance is often a joint responsibility between security teams and those responsible for governance, risk, and compliance within an organization. In smaller organizations, it often falls under a single team.
What Are the ISO 27001 Requirements?
ISO 27001 compliance requirements are outlined in Annex A, which contains 114 controls divided into 14 domains (called “clauses” by the ISO team). The domains are:
- Information security policies: Organizations should define security policies that apply across all systems and assets they own or manage.
- Organization of information security: Organizations should implement a specific framework for enforcing information security policies.
- Human resource security: Organizations should define security policies for employees, as well as outside stakeholders like vendors and partners.
- Asset management: Organizations should systematically manage the assets they own and implement adequate security controls for each one.
- Access control: Organizations must restrict access to the least necessary for employees to do their jobs.
- Cryptography: Organizations should use cryptographic techniques like encryption to protect sensitive data.
- Physical and environmental security: Organizations must ensure physical security for their assets.
- Operations security: This family includes a number of operational policies and procedures for organizations to follow when implementing security operations.
- Communications secrecy: Organizations must secure network communications.
- System acquisition, development, and maintenance: Security should be integrated into asset lifecycle management.
- Supplier relationships: Organizations must require reasonable security controls from their supplier and supply chains.
- Information security incident management: Organizations must implement effective procedures for responding to and reporting security incidents.
- Information security aspects of business continuity management: Organizations should establish procedures for maintaining business continuity in the wake of security incidents.
- Compliance: Organizations must determine which regulatory requirements govern them and make sure they take steps to comply with those laws
Not all of these are directly related to cloud security, Physical and environmental security, for example, and are therefore outside the scope of how Orca Security can support related efforts. However, many do have a direct connection to cloud security, and we’ll examine how Orca can help below.
8 Challenges with ISO 27001 Compliance Efforts
ISO 27001 compliance efforts can present several common challenges for organizations. These challenges can vary in complexity and impact depending on the size of the organization, its industry, and the specific context of implementation. Some common challenges include:
- Resource allocation: Implementing and maintaining ISO 27001 compliance can require dedicated resources, both in terms of time and personnel. Organizations often struggle to allocate the necessary staff and time for comprehensive compliance efforts.
- Complexity of implementation: ISO 27001 involves a comprehensive set of controls and processes that must be tailored to the organization’s specific needs. Navigating this complexity and customizing the controls to fit the organization’s environment can be challenging.
- Multi-cloud monitoring: Organizations that rely on cloud platform native security tools often need to maintain and align policies across disparate solutions, resulting in added time and tedious manual processes.
- Lack of expertise: Organizations might lack the necessary in-house expertise to effectively implement ISO 27001 requirements. This could include understanding the intricacies of the standard and the technical aspects of security controls.
- Friction between teams: Compliance can be fragmented and separate from cloud security teams responsible for security risk management, resulting in a lack of cohesion, efficiency, and friction.
- Ongoing maintenance and monitoring: ISO 27001 compliance is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous maintenance and improvement. Regularly updating policies, conducting risk assessments, and adapting controls to new threats and technologies demand ongoing commitment.
- Audit preparation: Preparing for ISO 27001 audits, both internal and external, requires meticulous organization of evidence, documentation, and implementation status. Organizations need to be ready to demonstrate their compliance effectively.
- Emerging threats and technologies: The threat landscape and technology landscape are constantly evolving. Adapting ISO 27001 controls to address emerging threats and technological advancements can be challenging. As cloud environments expand and change, continuous compliance efforts are needed to gain full visibility into security and compliance posture.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, a commitment to continuous improvement, and often, seeking external expertise. A cloud security and compliance platform like Orca can help automate the process and make it more efficient.
How Orca Security Helps Organizations with ISO 27001 Compliance
To help ease the challenges of ISO 27001 compliance, Orca’s central cloud security and compliance platform helps in several ways.
Independent Report on Orca’s ISO Compliance Support Capabilities
GRSee Consulting, an independent security and risk management consulting firm whose consultants are also ISO lead auditors, recently completed a report detailing how the Orca Cloud Security Platform enables organizations to meet ISO 27001 compliance requirements.
The report describes how the Orca Platform brings together core cloud security capabilities that support customers in meeting ISO 27001 requirements in diverse and dynamic environments, namely:
- Organization of information security: Orca provides a regular update with the new versions of information security best practices. This update can help Orca’s customers to comply with the information security controls of the ISO standard and to be aware of new vulnerabilities and methods of action to remediate them. This helps with the above challenge of ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
- Asset management: Orca provides a complete, multi-cloud inventory of all the assets in the cloud environment. Instead of relying on separate cloud service provider tools to measure compliance with different cloud provider CIS benchmarks, Orca’s multi-cloud security platform provides a compliance ‘HQ’ for all major compliance frameworks, including ISO 27001, thus easing the challenge of multi-cloud monitoring. As Orca’s visibility into cloud resources and prioritization of security risks is unified across cloud providers, so too are our compliance capabilities. This can help Orca’s customers to meet the ISO requirement of inventory of assets and ensure that each asset has effective protection and controls.
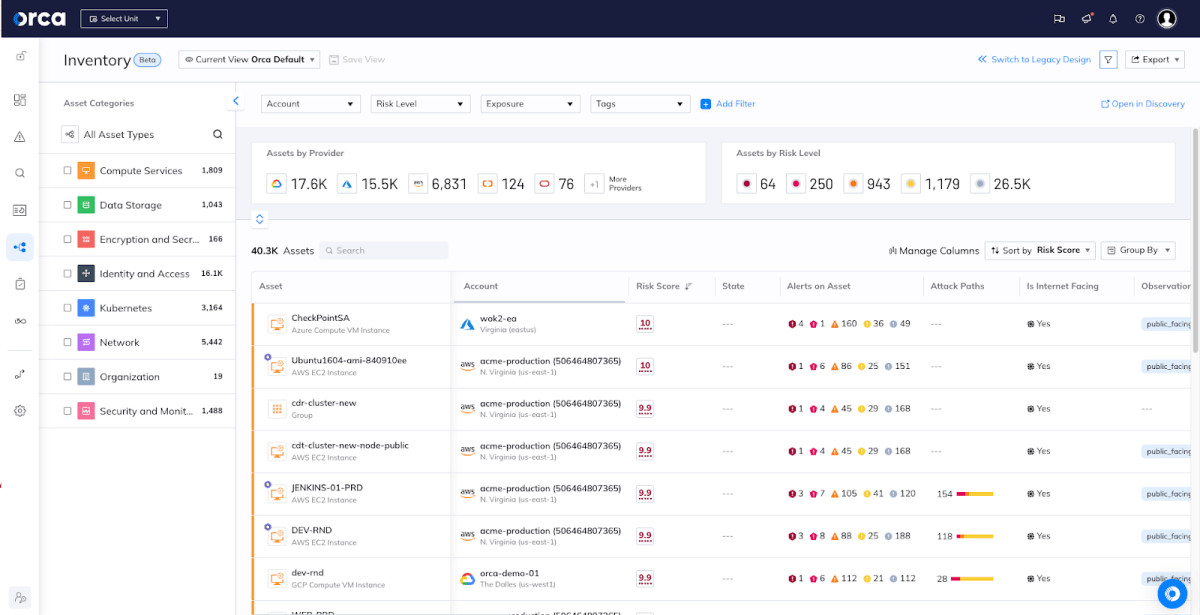
Orca’s multi-cloud Inventory dashboard provides extensive visibility
- Operations security: Orca performs daily malware and vulnerability scans, enabling companies to meet the controls against malware requirements under ISO 27001. This also ensures that any malware detected during the daily scan can be promptly addressed. This can help with several of the challenges mentioned above, including resource allocation, and ongoing maintenance and monitoring. Orca includes reporting features that can track compliance progress over time (as in, this asset that used to have a vulnerability has been patched), which can also alleviate the challenge of audit preparation.
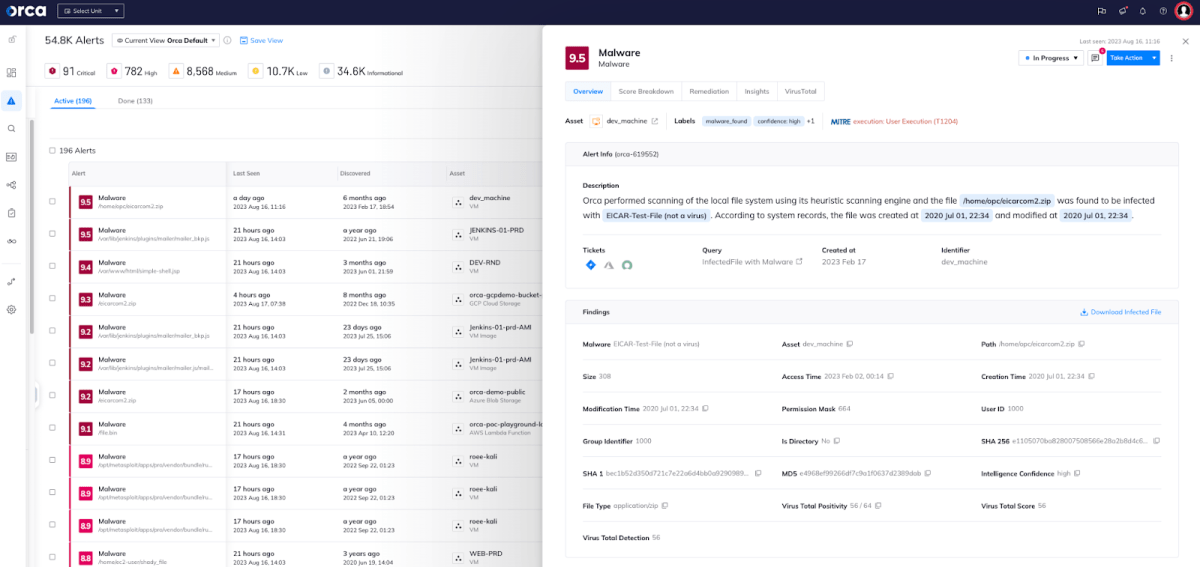
An Orca alert to malware discovered on a virtual machine
- Communications security: Orca helps their customers to control the network by mapping all the protocols and ports that the company uses and alerting in case there is a use in a weak protocol, such as FTP or an early TLS version, for transferring sensitive information over a public network.
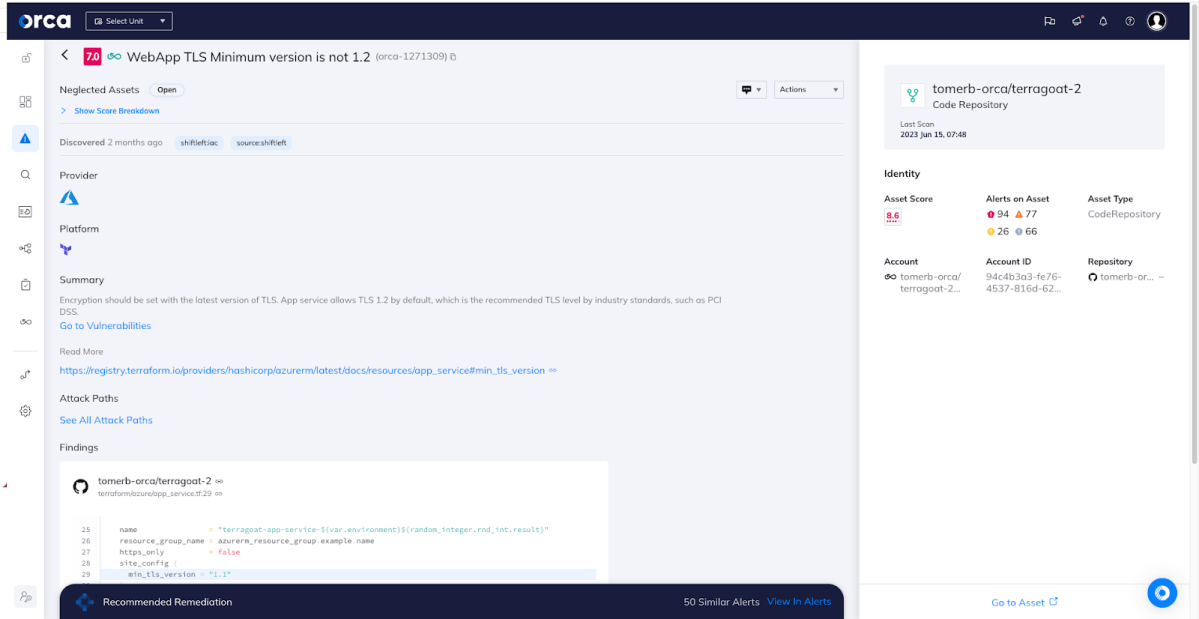
Orca alerts to an insecure TLS version
- System acquisition, development, and maintenance: Orca identifies code vulnerabilities during the software development process, allowing companies to prevent vulnerabilities from being released into production. In addition, Orca provides a Shift Left Security scanning for IaC (Infrastructure as Code) templates and container images, ensuring that vulnerabilities, secrets, misconfigurations, and malware are detected as early as possible. Linking security and development misconfigurations helps to strengthen communication between teams and reduce friction.
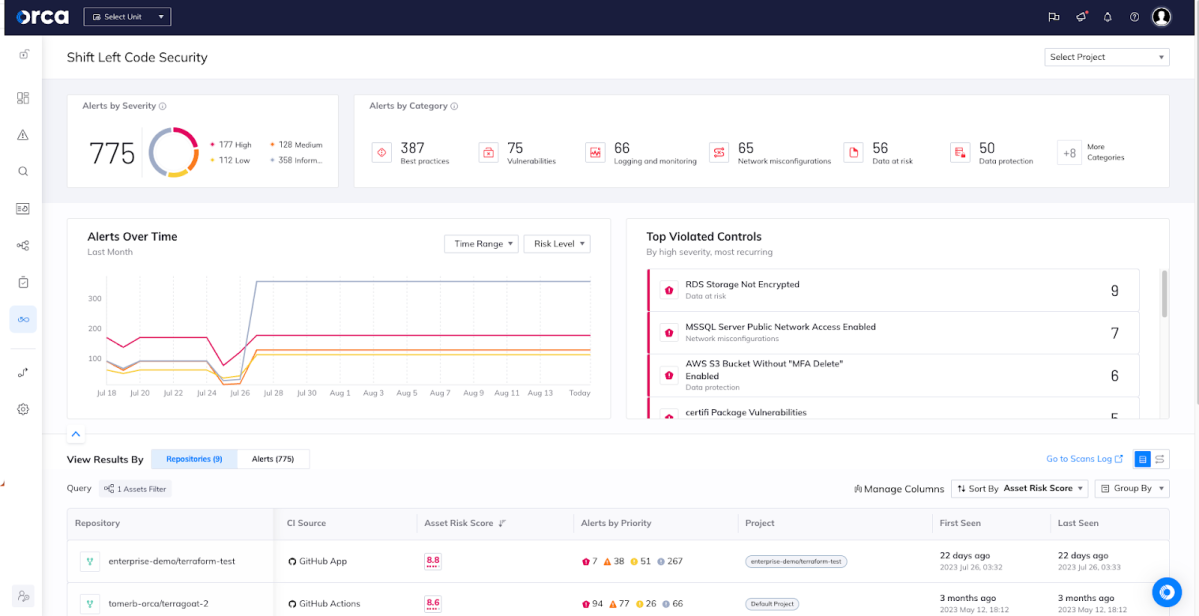
Orca’s Shift Left Code Security dashboard
All Compliance Results in One Place
With an easy to use compliance dashboard that provides actionable metrics, compliance teams can know where they stand in meeting ISO 27001 requirements, and have the actionable data they need to stay ahead of audits.
Leveraging Orca’s ability to identify cloud risks—including misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, malware, identity and access management excessive privileges, lateral movement risks, sensitive data at risk, and exposed APIs—security teams are able to see which compliance checks have resulted in fully automated “passed” or “failed” results. These include compliance checks across the entirety of cloud assets, including VMs, containers, images, serverless functions, storage buckets, network configurations, identities, data, and more.
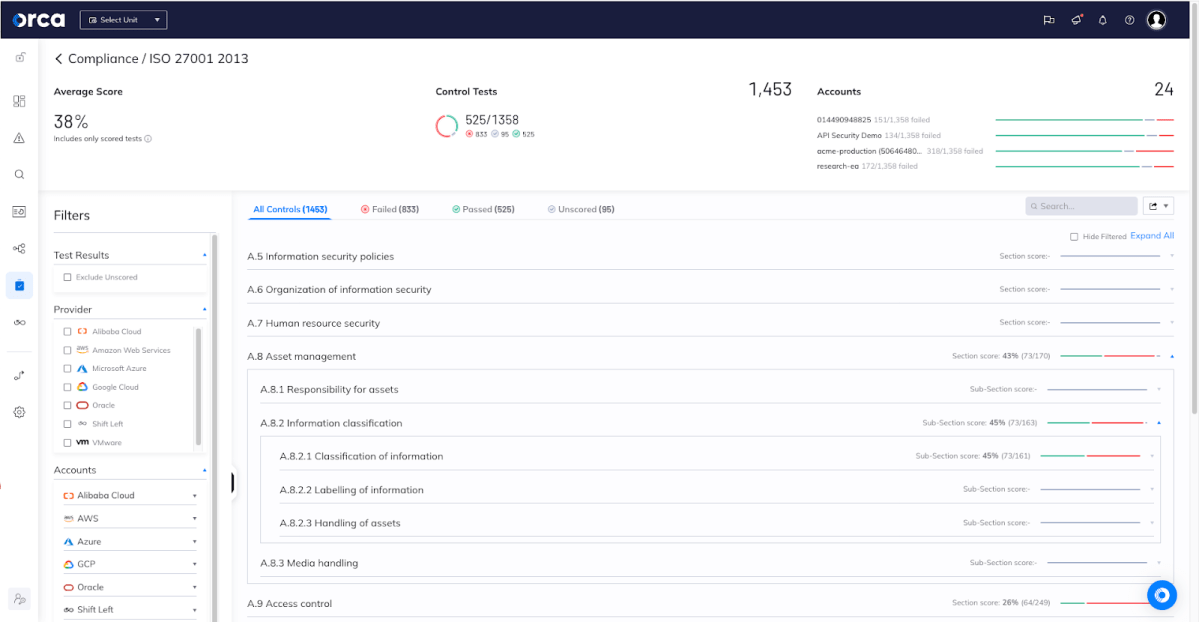
Regular tests help organizations address issues timely to maintain compliance
It’s important to note that Orca performs that security and compliance policies in all cloud provider platforms are aligned. Orca directly links compliance gaps with specific security alerts, allowing governance and compliance teams to not only understand a particular compliance check has failed result, but to have the necessary information to remediate the risk and improve compliance results.
For example, in the screenshot below, you can see that the “A.9.2.3 Management of privileged access rights” control—which provides guidelines on managing more powerful and higher ‘privileged’ levels of access e.g. systems administration permissions versus normal user rights—is linked to Orca alerts about a user with privilege escalation permissions without MFA enabled.

Failed compliance checks are directly linked to Orca-discovered security risks
Within each alert are clear remediation instructions to reduce the attack surface and tighten compliance. In addition, compliance teams can use Orca’s auto-remediation capabilities to reduce Mean Time to Remediation (MTTR) to the bare minimum, thereby improving your security posture and compliance requirements.
To communicate with both internal stakeholders and auditors, Orca generates comprehensive reports to allow teams to easily understand and communicate which controls need to be addressed to improve compliance posture and report on their progress. This helps with the challenge mentioned earlier of audit preparation, as Orca is able to provide clear evidence of compliance.
Customize Compliance Frameworks to Fit Specific Needs
Orca provides the ability to customize particular controls of the ISO 27001 framework. While the framework has extensive security guidelines, they are not specifically tailored for cloud environments, and so an organization will choose to supplement the framework with additional controls.
To provide complete flexibility, users have the option of using framework templates. Templates enable users who wish to make small changes to an existing framework or combine rules from two or more frameworks.
This means that your compliance tests can be customized to your environment for improved accuracy, fewer false positives, and ultimately greater trust in the results.
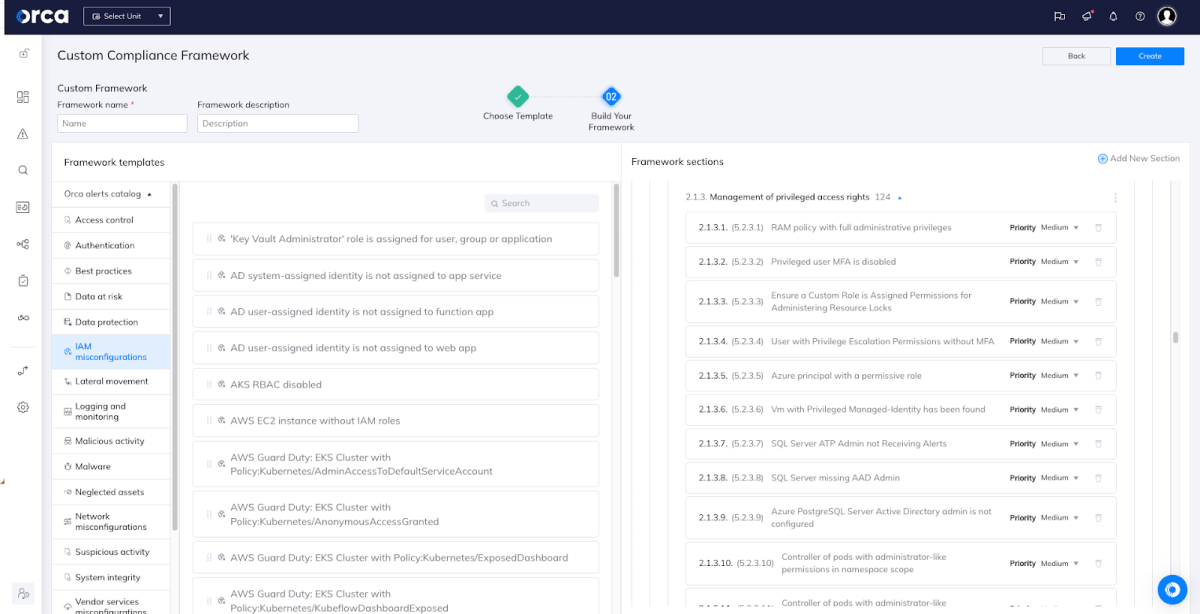
Orca allows for compliance framework customization
Learn More about Orca’s Compliance Value
To learn more about how Orca simplifies compliance efforts and helps maintain a strong cloud security posture, read our blog Taking the Pain Out of Cloud Compliance. To read about each ISO 27001 control that Orca helps organizations meet, download the GRESee Consulting assessment Meet ISO 27001 Requirements with the Orca Cloud Security Platform.
We’re also proud to announce Orca recently achieved Center for Internet Security® (CIS®) Benchmarks certification across 24 cloud frameworks. This certification attests that the platform accurately identifies any configurations that deviate from recommended best practices in over 60 CIS Benchmarks. Learn more here.
You can also reach out to us to schedule a demo.



