Table of contents
Forecasts predict the global market for cloud security to reach more than $124 billion (USD) by 2034, a significant increase from the estimated value of $40 billion in 2025. At a time when cloud computing represents a requirement for competitive advantage, understanding cloud security is paramount to any organization and tech leader.
Cloud security encompasses the technologies and practices that protect your cloud-based systems and data from evolving security risks. With cyberthreats becoming more sophisticated and cloud services growing more susceptible to exploitation, organizations need robust and resilient security measures.
In this post, we dive deep into the topic of cloud security, exploring its key components, benefits, challenges, and best practices. From identity management to encryption, discover the tools and techniques needed to fortify your cloud environment.
Introduction to cloud security
What is cloud security?
Cloud security refers to the comprehensive set of measures, controls, and policies designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure associated with cloud computing. As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, understanding and implementing robust cloud security practices has become paramount. Cloud security encompasses various strategies to safeguard cloud environments against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
Cloud security plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information and maintaining business continuity. Modern enterprises rely heavily on cloud services for innovation, daily operations, and a number of mission-critical functions, illustrating the immense importance of protecting them. By implementing strong cloud security measures, businesses can:
- Protect sensitive data and intellectual property.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations and industry regimes.
- Maintain customer trust and brand reputation.
- Minimize downtime and potential financial losses.
Overview of cloud security threats
As cloud adoption continues to grow, so does the sophistication of threats targeting cloud environments. Some common cloud security challenges include:
- Data breaches
- Insider threats
- Misconfigured cloud services
- Account hijacking
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
Key components of cloud security
Cloud security encompasses several critical components that work together to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments. Understanding these key elements is crucial for implementing effective cloud security strategies and protecting your cloud assets.
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the cornerstone of cloud security, controlling who can access your cloud resources and what actions they can perform. It involves user authentication, authorization, and access control policies. Implementing strong IAM practices helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of data breaches.
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) can help you gain visibility into the data you store and process by providing capabilities to automatically discover, classify, and de-identify regulated cloud data. DLP technologies safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, or transmission. They monitor and control data in motion, at rest, and in use, helping organizations comply with regulations and protect intellectual property. DLP is essential in addressing cloud security challenges related to data protection and privacy.
3. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze log data from various sources across your cloud infrastructure. They provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities. SIEM is crucial for maintaining visibility into your cloud environment and identifying potential security threats.
4. Encryption and data protection
Encryption is a fundamental aspect of cloud security, ensuring data confidentiality both in transit and at rest. It involves using cryptographic algorithms to convert data into unreadable formats, protecting it from unauthorized access.
2025 State of Cloud Security Report
Key findings and trends
The 2025 State of Cloud Security Report reveals a cloud security landscape defined by rapid innovation and rising complexity. As organizations embrace multi-cloud and AI-driven environments, the scale and interconnectivity of risks continue to expand.
More than half of organizations (55%) now use two or more cloud providers, and 84% use AI in the cloud, yet 62% have at least one vulnerable AI package. Traditional risks persist as well: nearly a third of all cloud assets remain neglected or unpatched, and each contains an average of 115 vulnerabilities. Data exposure is also on the rise, with more than a third of organizations leaving sensitive databases publicly accessible.
These findings underscore the Defender’s Paradox: attackers need to be right only once, while defenders must secure every path. In fact, 13% of organizations have a single cloud asset responsible for more than 1,000 attack paths, highlighting the need for unified visibility, contextual prioritization, and AI-driven defenses across the entire application lifecycle.

Report
2025 State of Cloud Security
Key recommendations
The report also summarizes key recommendations on how organizations can reduce their cloud attack surface and harden their environments. This includes the following activities:
- Secure AI while leveraging it for defense: Protect your environment from AI-related risks by securing models, data, and dependencies using cloud security best practices. At the same time, use AI to enhance detection, remediation, and least-privilege enforcement..
- Protect high-value assets: Continuously identify and monitor your organization’s “crown jewels.” Prioritize remediation of the attack paths that endanger them, ensuring real-time protection for sensitive and business-critical resources.
- Safeguard sensitive data: Locate where sensitive data resides across your cloud estate and apply the appropriate controls to keep it secure and compliant. Continuously monitor for unusual access or exfiltration attempts.
- Prevent workload neglect: Maintain a current inventory of workloads and monitor for unpatched or abandoned assets. Deploy only supported applications and operating systems, and enforce IaC security benchmarks before deployment.
- Prioritize patching strategically: Focus on remediating critical vulnerabilities that are exploitable in runtime rather than attempting to patch everything. .
- Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Grant users and non-human identities only the minimum permissions needed. Use automation and AI-driven IAM capabilities, including Just-in-Time (JIT) Access, to reduce standing privileges and enforce least privilege at scale.
- Unify security before deployment and during runtime: Implement security that combines runtime protection with pre-deployment security scanning. Detect and remediate issues earlier in the application pipeline, trace production alerts back to source code, and maintain full visibility across the application lifecycle.
- Continuously audit and monitor: Conduct regular audits, enforce security baselines, and continuously monitor access logs for anomalies to detect and respond to threats faster.
Cloud security challenges
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud technologies, they face several significant hurdles in maintaining robust security. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective cloud security measures and safeguarding your digital assets.
Lack of visibility
One of the biggest cloud security issues that firms face is a lack of visibility into their cloud environments, which include digital assets, infrastructure, and data. Unlike on-premise infrastructure, cloud environments are dynamic and constantly changing, with more users able to create ephemeral resources such as containers and serverless functions that demand protection and expand an organization’s attack surface. This makes it difficult for security teams to gain or maintain visibility into their cloud environments, not to mention adequately secure them.
Multi-tenancy issues
Multi-tenancy problems develop when multiple customers share the same cloud infrastructure, which may raise distinct security risks. While cloud companies take precautions to protect customer data, the risk of data loss or unauthorized access remains a concern. A vulnerability in one tenant’s environment could expose others to possible intrusions, making multi-tenancy a major challenge in cloud security. Organizations must therefore carefully assess their cloud provider’s safety measures in order to offer proper protection in shared environments.
Access management and shadow IT
Managing user permissions across cloud services can be challenging, especially with the use of multiple vendors and platforms. The rise of remote work and distributed teams adds to this complexity. Additionally, the ease of adopting cloud services has led to an increase in shadow IT, where employees use unapproved applications. This can jeopardize data security and compliance, as these unsanctioned tools are often neglected or poorly protected.
To effectively manage access in a cloud environment, companies must address the challenges posed by shadow IT and ensure that all software used by employees is approved and secure. This approach not only helps protect data but also ensures compliance with relevant standards.
Compliance and regulatory concerns
Adhering to industry regulations and data protection laws becomes more challenging in cloud environments. Organizations must ensure their cloud providers meet specific compliance requirements and implement appropriate controls to protect sensitive data. This is particularly crucial when dealing with cross-border data transfers and varying international regulations.
Misconfigurations and human error
Cloud security challenges often come from simple misconfigurations or human mistakes. The complexity of cloud systems and the rapid pace of changes can easily lead to overlooked security settings or incorrect access controls. These missteps create vulnerabilities that bad actors might exploit, underscoring the need for strong security practices and continuous monitoring.
Types of cloud security solutions
Cloud security refers to a broad range of technologies, philosophies, and vendors. Various types of cloud security solutions exist, and each one presents significant differences that can greatly impact your overall security.
Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid Cloud Security
When discussing cloud security, understanding the security implications of different cloud deployment models is crucial. Think of it like choosing your living arrangement:
- Public cloud security is akin to living in an apartment building where everyone shares the same resources. In this setup, companies depend on shared infrastructure provided by major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure. While these providers invest heavily in security measures, the responsibility for securing data ultimately lies with each business. For example, a startup might choose a public cloud to host its application, but it must implement robust access controls and encryption to keep customer data secure and private.
- Private cloud security resembles owning a standalone house. Here, organizations gain exclusive control over their infrastructure, allowing them to customize security measures to meet their specific needs. This model is particularly beneficial for industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare or finance. For instance, a financial institution might select a private cloud to ensure that customer financial records are stored securely and comply with regulations like PCI DSS.
- Hybrid cloud security offers flexibility similar to having a primary residence and vacation home. In this model, businesses can store sensitive data in a private cloud or on-prem environment while leveraging the scalability of a public cloud for other operations. For example, a retail company might keep customer payment data in a private cloud for added security while using a public cloud for marketing analytics. This approach requires a unified security strategy to effectively protect data across all environments.
AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM)
AI Security Posture Management is an emerging field focused on mitigating security risks and compliance challenges related to the use of AI models. It encompasses a range of strategies, solutions, and practices aimed at helping organizations utilize AI models and large language models (LLMs) safely in their operations.
API Security
API Security safeguards APIs against threats, vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, exposures, and various other risks. This field integrates strategies, solutions, and practices aimed at continuously discovering and cataloging APIs (including shadow APIs), detecting and addressing API-related risks, and tracking both newly added and removed APIs, as well as any API drift.
Application Security
Application Security encompasses a set of cloud security strategies, technologies, and practices that integrate security and testing into the early stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). This approach aims to identify and resolve security risks and issues before applications are deployed to production, making it more cost-effective to address problems early on.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM)
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM) is a cloud security solution focused on managing access rights and permissions for cloud resource entities. CIEM (pronounced “KIM”) solutions are essential for enforcing the principle of least privilege (PoLP), a security approach that gives users access only to the resources necessary for their specific job functions.
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR)
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) is a segment of cloud security dedicated to identifying active attacks within cloud environments and equipping organizations with the insights and tools necessary for security teams to investigate and respond effectively.
The primary goal of CDR is to detect cloud attackers who have circumvented the perimeter defenses of cloud resources and applications. By consistently delivering contextualized data on potential malicious activity to security operation center (SOC) and incident response (IR) teams, CDR enhances the speed and effectiveness of investigations and responses to cloud-based attacks.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
A Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) is a cloud security solution designed to provide extensive coverage and visibility across multi-cloud environments, while also identifying risks throughout the entire technology stack. This encompasses issues such as cloud misconfigurations, poorly managed identity access, vulnerabilities, and insecure workloads.
Recognized as a distinct cloud security category by Gartner in 2020, CNAPPs have emerged as a modern alternative to many traditional cloud security tools, consolidating their various functionalities into a single platform. This includes features from Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP), Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM), as well as other solutions like compliance tools, API Security, and Data Security Posture Management (DSPM).
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) allows organizations to detect and address risks, misconfigurations, and compliance violations within their cloud infrastructure, helping to minimize their attack surface. CSPMs can detect and remediate numerous types of misconfigurations, such as internet-exposed virtual machines and storage buckets, reliance on default settings from cloud providers, open ports not utilized by other applications in the infrastructure, and much more
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
A Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is a cloud security solution specifically focused on securing server workloads in the public cloud. CWPP solutions identify and detect risks within cloud workloads, such as vulnerabilities, malware, and sensitive data exposure. These capabilities can be provided either through standalone solutions or as part of a unified CNAPP.
Compliance
Compliance solutions support organizations in meeting regulatory frameworks and industry standards related to their use of public cloud environments. These solutions facilitate and automate essential tasks, such as identifying, monitoring, addressing, and reporting on cloud security risks on an ongoing basis.
Container and Kubernetes Security
Container and Kubernetes Security is a segment of cloud security aimed at improving the security of containerized applications and Kubernetes environments. This involves the implementation of various security practices, including secure cluster configurations, access control, container image security, network protection, and ongoing monitoring.
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM)
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) is a cloud security solution that detects sensitive data at risk, prioritizes alerts, and facilitates the remediation of any associated security risks and compliance issues.
Disaster recovery and business continuity
Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer robust protection against data loss and system failures. These solutions ensure business continuity by replicating data and applications across multiple locations, allowing for quick recovery in case of disasters or cyberattacks.
Real-time runtime protection
Real-time runtime protection solutions provide continuous visibility, detection, and alerting for active workloads, enabling organizations to identify and respond to threats as they occur. By analyzing runtime activity and system behavior, these solutions can alert on or automatically terminate malicious processes to prevent escalation or compromise. They typically require the installation of a lightweight sensor on sensitive workloads, ensuring comprehensive protection for high-value systems while minimizing operational overhead.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management involves identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues within an organization’s IT systems and infrastructure. In cloud environments, vulnerability management emphasizes maintaining visibility and control over the security of cloud services and applications, enabling organizations to address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
Best practices for implementing cloud security
Implementing robust cloud security measures is crucial for protecting your organization’s data and assets in the cloud. By following these best practices, you can significantly enhance your cloud security posture and mitigate potential risks.
Focus on comprehensive coverage and risk detection
You can only protect what you can see. Equip your security teams with advanced tools that provide complete visibility into your cloud environments, including any containers and serverless functions that users may add in the future. Combine this with technology that detects all types of cloud security risks, as these dynamic environments can be vulnerable to various interconnected threats. This comprehensive approach helps you counter attackers’ freedom of movement and multi-phased attacks effectively.
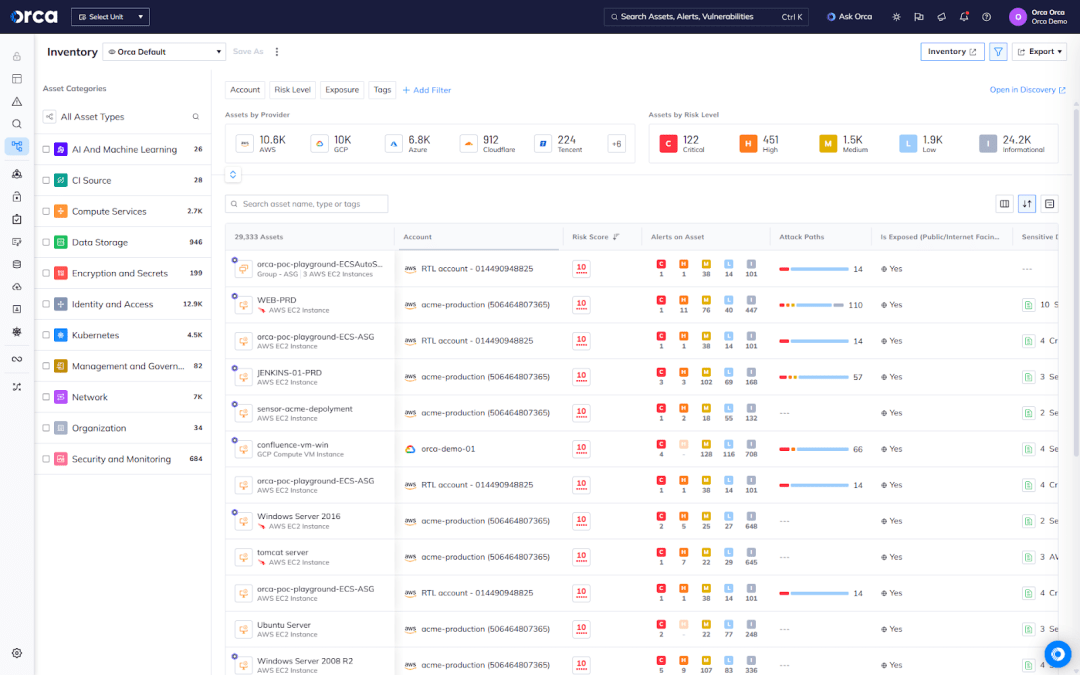
Configure your settings
No two cloud environments are alike. Each organization has unique needs when it comes to cloud security, so don’t take a one-size-fits-all approach. After acquiring advanced cloud security technology, tailor it to align with your specific goals and conditions. For instance, configure features that automate processes, customize alerts for specific risk types, and enable ready-made compliance templates to enhance your security posture effectively. Also, configure any preventative settings in your cloud security solution that block issues in development and prevent them from reaching production.

Leverage integrations and minimize cross-functional friction
In many organizations, tensions often run high between development, DevOps, and security teams. Security teams depend on developers to resolve issues, while developers grapple with tight timelines and the pressure to deliver code quickly. These interactions typically require developers to fix problems when they are most costly and time-consuming. To alleviate this friction, leverage integrations that make it seamless for security and development teams to collaborate. Best practice is to take advantage of integrations that allow developers to use their existing tools and processes, eliminating the need to learn or login to a separate platform.
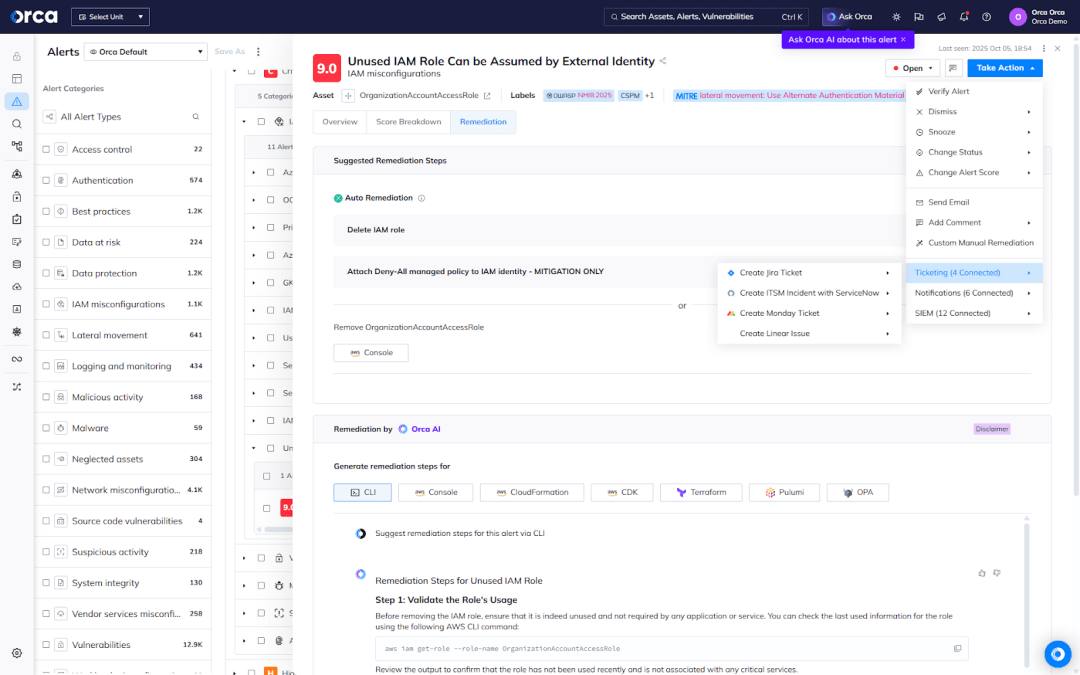
Protect high-value assets with real-time detection and monitoring
Adding real-time runtime protection to your most sensitive workloads is a practical way to strengthen your overall cloud defense. While this type of security doesn’t provide complete visibility or address hygiene issues such as misconfigurations or overprivileged identities, it serves as a powerful safeguard against active threats. By continuously monitoring runtime behavior and detecting potential threats and activity, it enables organizations to prevent attacks from escalating into severe incidents.

Treat compliance as a continuous requirement
Compliance drift—when organizations gradually stray from adhering to standards and controls—is a common challenge. This often occurs when companies view compliance as a one-time event focused solely on passing audits, rather than an ongoing responsibility that reflects their security effectiveness. As a result, they waste valuable time and resources scrambling to prepare for audits or managing the fallout from violations. To combat this, embrace compliance as a continuous process. This means not only leveraging advanced technology to automate tasks and processes but also prioritizing compliance as an ongoing business objective.

Educate staff
Train your staff on cloud security best practices and potential risks. Hold regular training sessions to keep employees informed about the latest threats and security protocols. Building a security-conscious culture within your team is vital for maintaining a strong cloud security posture.
By adopting these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Keep in mind that cloud security is an ongoing process that demands continuous attention to evolving threats and technologies.
The future of cloud security
AI-driven solutions are set to enhance and expand existing capabilities while alleviating the burden on overwhelmed security teams. These technologies now offer features that make it easier for users to navigate their cloud environments, understand the assets and risks within them, and accelerate remediation efforts to reduce the mean time to remediation (MTTR) and prevent critical incidents.
However, AI innovation continues to challenge cloud security. Emerging solutions enable organizations to monitor, detect, and remediate security risks associated with their cloud providers’ AI services, as well as the AI models and packages available in their environments. The Orca 2024 State of AI Security Report highlights the prevalence of AI risks in cloud ecosystems. The future promises further innovation in both AI risks and security tools.

Report
2025 State of Cloud Security
Command your cloud with Orca
Orca offers a unified and comprehensive cloud security platform that identifies, prioritizes, and remediates security risks and compliance issues across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and Kubernetes. The Orca Platform leverages Orca’s patented SideScanning™ technology to provide complete coverage and comprehensive risk detection.
To see the Orca Platform in action, schedule a personalized demo with one of our experts.
Conclusion
As the cloud security market continues to expand rapidly, organizations must prioritize safeguarding their cloud environments to maintain a competitive edge. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the growing reliance on cloud services underscore the need for comprehensive security strategies. You can significantly enhance your organization’s cloud security posture by implementing robust security measures, staying informed about emerging threats, and leveraging cutting-edge technologies.
With the right tools and commitment, you can confidently leverage the power of the cloud while upholding the highest security and compliance standards.
FAQs
Why is cloud security important?
Cloud security is of paramount importance in modern enterprises due to the increasing reliance on cloud-based services and infrastructure. As organizations migrate their data and applications to the cloud, they face new challenges in protecting sensitive information from cyber threats. The importance of cloud security lies in its ability to safeguard critical assets, maintain business continuity, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Effective cloud security measures help prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and service disruptions that could lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. By implementing robust cloud security practices, companies can confidently leverage the benefits of cloud computing while mitigating associated risks.
What are the types of cloud security solutions?
There are several types of cloud security solutions. While not an exhaustive list, some of them include:
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM): Manages access rights and permissions for cloud resources, enabling the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to ensure users access only what they need.
- Cloud Detection and Response (CDR): Detects attackers who breach cloud security controls, providing continuous monitoring and alerts for malicious activity, allowing security teams to respond to ongoing threats.
- Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP): Offers comprehensive coverage of multi-cloud environments, consolidating various security solutions into one platform for effective risk detection, prioritization, and remediation.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Identifies and addresses risks, misconfigurations, and compliance violations in cloud infrastructure, helping to minimize the attack surface.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP): Secures server workloads in the public cloud by detecting risks such as vulnerabilities, malware, and exposed sensitive data.
Is cloud security the same as cyber security?
Cybersecurity covers all forms of digital protection. Cloud security focuses on protecting data, applications, and infrastructure associated with cloud services, while also dealing with issues like multi-tenancy, shared responsibility models, and cloud-specific risks. Cloud security is an essential component of an organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy, especially as more businesses adopt cloud technologies to drive innovation and efficiency.




