Table of contents
According to Gartner, global spending on AI software will grow to $298 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.1%. Meanwhile, other studies predict the market value for AI security solutions to reach $141 billion by 2032 (CAGR of 24.2%). Clearly, organizations and industries everywhere are embracing AI technology to drive innovation and competitive advantage. Yet, we also see a distinct recognition of the importance of AI Security — and for good reason.
In this comprehensive guide, we dive deep into the topic of AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM), exploring what it entails, why organizations need it, and how you can best leverage it in your organization.
AI-SPM Defined
Many of the security risks facing AI models and LLMs are similar to other cloud assets, including limited visibility, accidental public access, unencrypted sensitive data, shadow data, and unsecured keys. AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM) solutions exist to help organizations mitigate these security risks and protect their AI innovation at scale.
What is AI-SPM?
AI security posture management (AI-SPM) is an area of cloud security focused on securing the infrastructure of machine learning (ML) and AI systems, models, packages, and data. AI-SPM solutions detect risks commonly affecting other cloud assets, including misconfigurations, overprivileged permission, Internet exposure, and more.
However, AI-SPM solutions also cover use cases unique to AI security, such as detecting sensitive data in training sets, which can lead to unintentional exposure through the legitimate use of an AI service. For all risks that fall within its purview, AI-SPM solutions help security teams remediate issues through automated features and capabilities.
AI-SPM also helps ensure compliance with regulatory mandates and industry standards. This includes ongoing compliance monitoring and reporting.
How AI-SPM works
AI-SPM involves the following activities, which occur continually:
Inventory AI resources
AI-SPM provides full visibility into all your deployed AI resources, including models, packages, data, and shadow AI. These solutions continually scan your cloud environments to detect existing and new AI projects, ensuring your security teams remain aware of all AI projects in your environment(s). By providing full visibility, AI-SPM solutions create the conditions for effectively securing AI resources and activities.
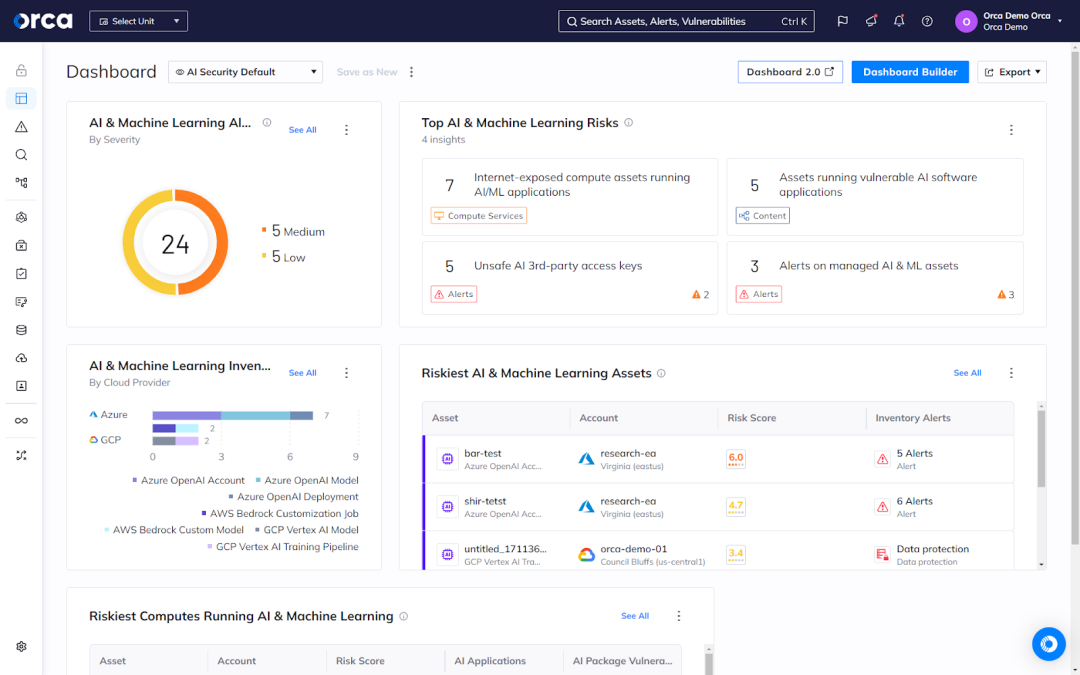
Detect and prioritize AI risks
In addition to full coverage of your AI footprint, AI-SPM technology also detects security risks associated with your AI models and resources. Advanced solutions prioritize detected risks by analyzing them dynamically using multiple factors. These may include access restrictions, exploitation impact, exploitation complexity, and more.
AI-SPM solutions then assign a severity score to the risk and generate an alert that prioritizes it accordingly. Ideally, AI-SPM solutions should adjust this severity score automatically and continually as risk factors change (e.g., when an AI resource no longer contains sensitive information).
In terms of the types of risks AI-SPM solutions can detect, most scan for misconfigurations in network security, data protection, access controls, and IAM (identity and access management). They also alert security teams if any AI models or training data contain sensitive information so they can take appropriate action to prevent unintended exposure.
Additionally, some sophisticated AI-SPM solutions also detect when access keys and tokens to AI services and software packages are unsafely exposed in code repositories. These solutions scan code repositories to find leaked AI access keys. Exposed keys can grant attackers access to AI models and their training data, allowing them to make API requests, tamper with the AI model, and exfiltrate data.
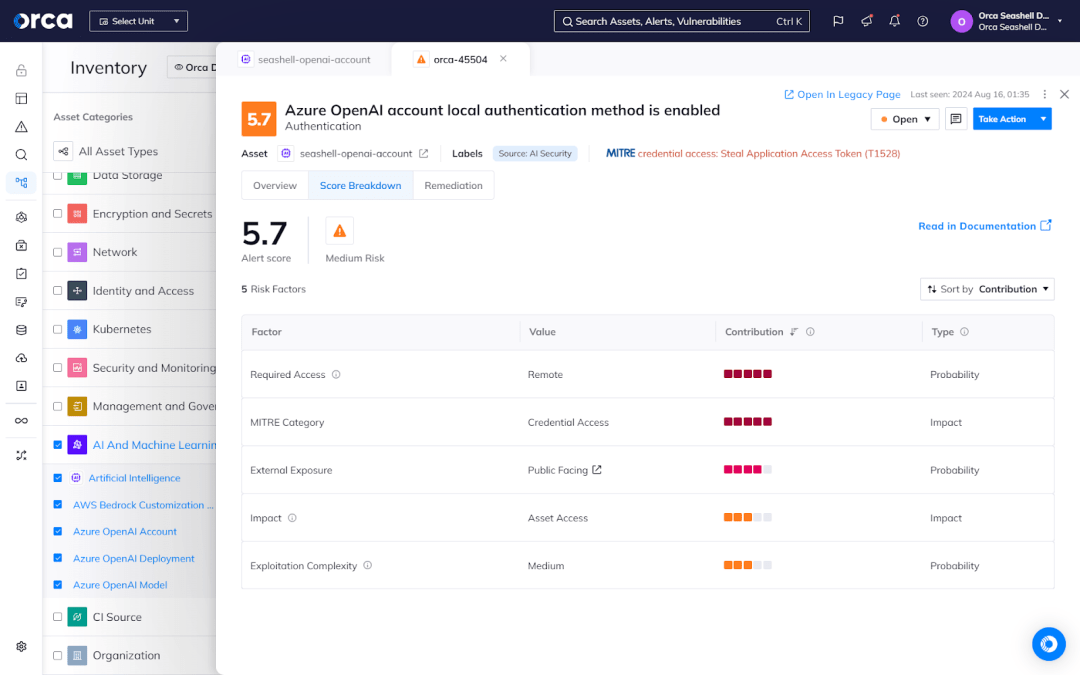
Remediate AI security risks
In tandem with risk detection, AI-SPM solutions also assist teams with remediation. Commonly, this takes the form of suggested remediation instructions. Some AI-SPM tools take this a step further by offering the ability to auto-remediate risks, or streamline the remediation process using generative AI (GenAI).
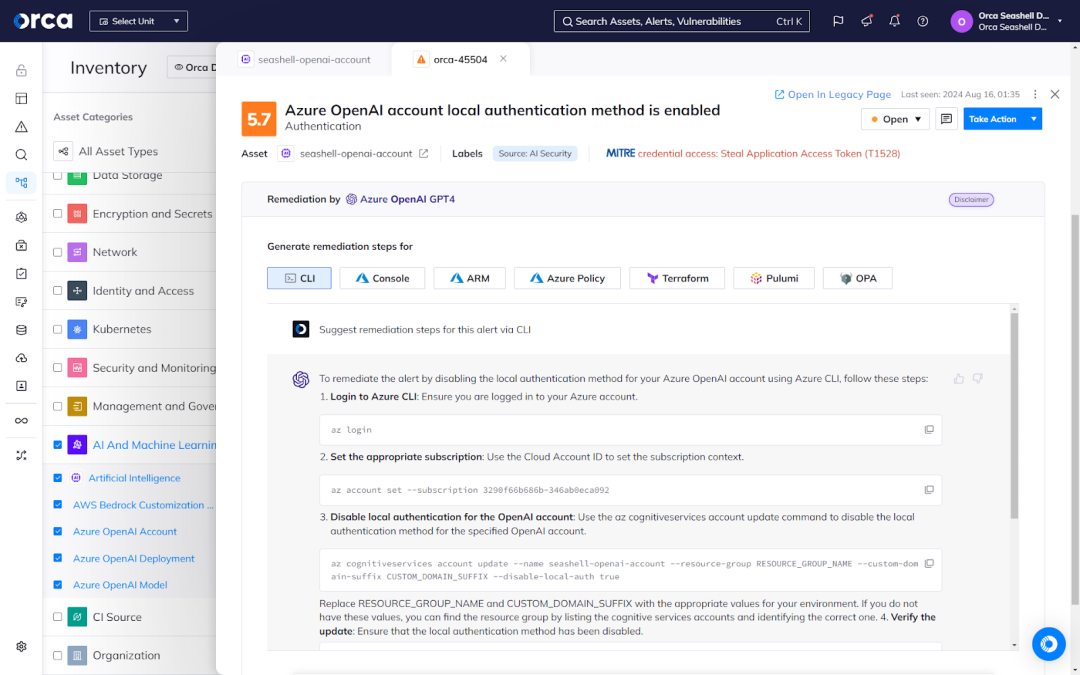
Security teams often assign remediation tasks to development or DevOps teams. Many AI-SPM solutions help facilitate this process through integrations with popular ticketing systems, communication applications, and productivity platforms. Solutions that offer these integrations also commonly notify security personnel when issues are resolved.
For example, the Orca Cloud Security Platform supports two-way integrations with Jira and ServiceNow. This enables security teams to create tickets for AI-SPM alerts without ever leaving the Orca Platform, while allowing developers to resolve the issue without ever using Orca. Once developers close a ticket, Orca rescans the issue, verifies it’s resolved, and then closes the ticket in the Orca Platform. If Orca determines an issue remains outstanding, it reopens and reassigns the closed ticket in the appropriate ticketing system.
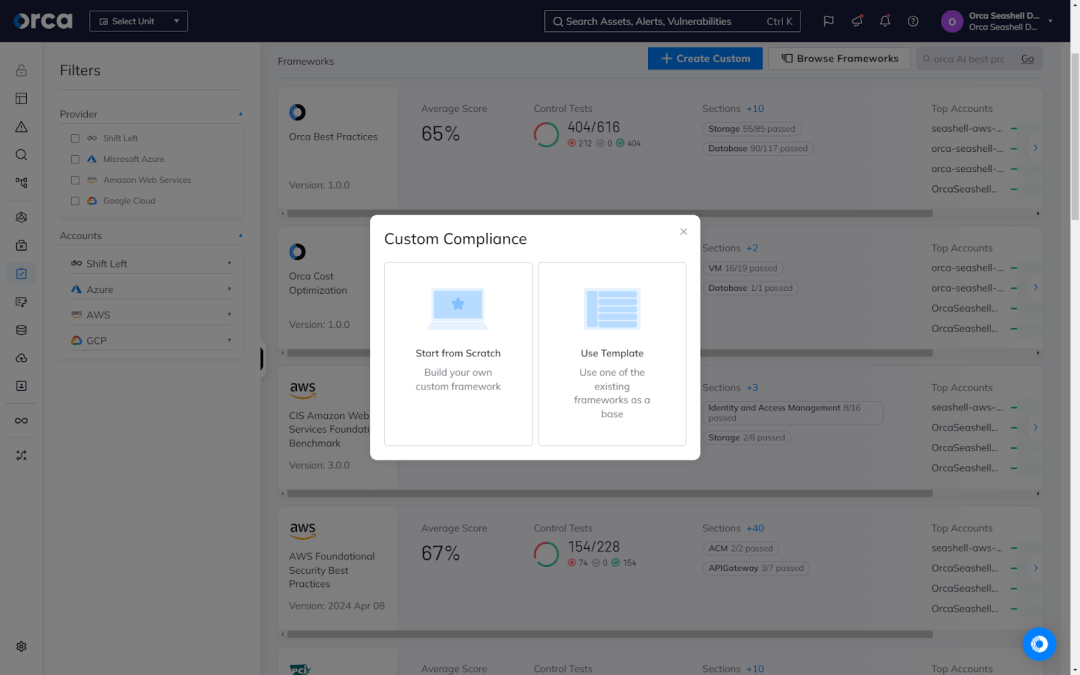
Facilitate compliance monitoring and reporting
Compliance is an essential use case of AI-SPM, helping organizations preserve their authority to operate. While the regulatory landscape governing AI is still emerging, organizations can expect to see new regulations in the relatively near future. For example, the European Union enacted the AI Act in 2024, which represents the first legal framework governing the responsible development and use of AI.
AI-SPM solutions can help enhance and automate compliance efforts. These solutions often facilitate adherence to standards by correlating security risks with regulatory controls, enabling teams to remediate areas of non-compliance. Other features commonly include continuous compliance monitoring and reporting. More advanced solutions tend to extend these capabilities to offer the ability to create and leverage custom frameworks, build automation workflows for streamlining tasks, integrate tasks with third-party platforms and tools, and schedule recurring reports.
Key components of AI-SPM
Cloud coverage
When it comes to cloud security, you can only protect what you can see. The same holds true in AI security. The ability to detect shadow AI, managed and unmanaged AI models, and every deployed AI resource is a prerequisite to ensuring their security. That’s why AI-SPM must have the ability to identify and scan all AI resources in your cloud estate.
Comprehensive risk detection
Like other cloud assets, AI resources are susceptible to a variety of different security risks, from misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, to sensitive data and IAM risks, to lateral movement and malware risk, and more. Yet these assets also face a unique set of risks, such as data poisoning, model theft, model skewing, and more. AI-SPM solutions should protect against each of these threats through comprehensive risk detection and mitigation. For example, these solutions should alert security teams of AI models exposed to the Internet, API keys stored in public repositories, resources that contain sensitive information, and more.
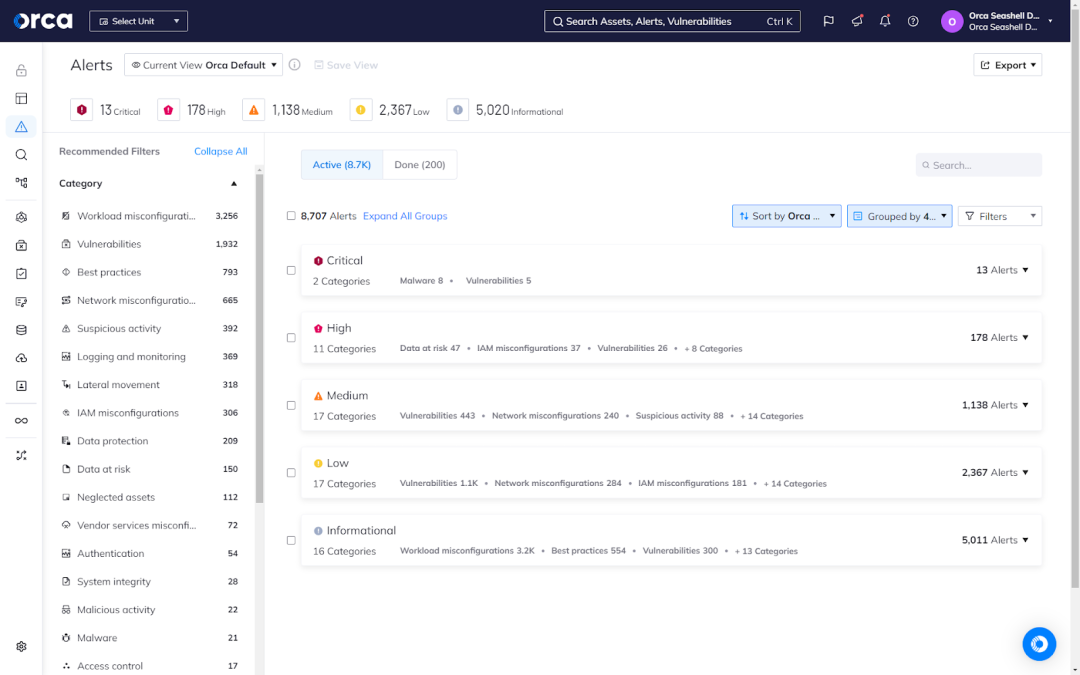
Dynamic risk assessment and prioritization
As mentioned previously, dynamic risk assessment and prioritization is a core capability of an effective AI-SPM solution. This enables security teams to focus their attention on the risks demanding immediate attention and resolution, enhancing security, limiting risk exposure, and reducing alert fatigue.
Integrations and automations
AI-SPM solutions solve a limited set of problems in the vast and connected ecosystem of cloud computing. Because of this, these tools must integrate with other solutions commonly featured in an organization’s security stack (e.g., other cloud security solutions, SIEM or SOAR systems, etc.), as well as other applications closely connected to the work of security teams (such as ticketing systems used by developers).
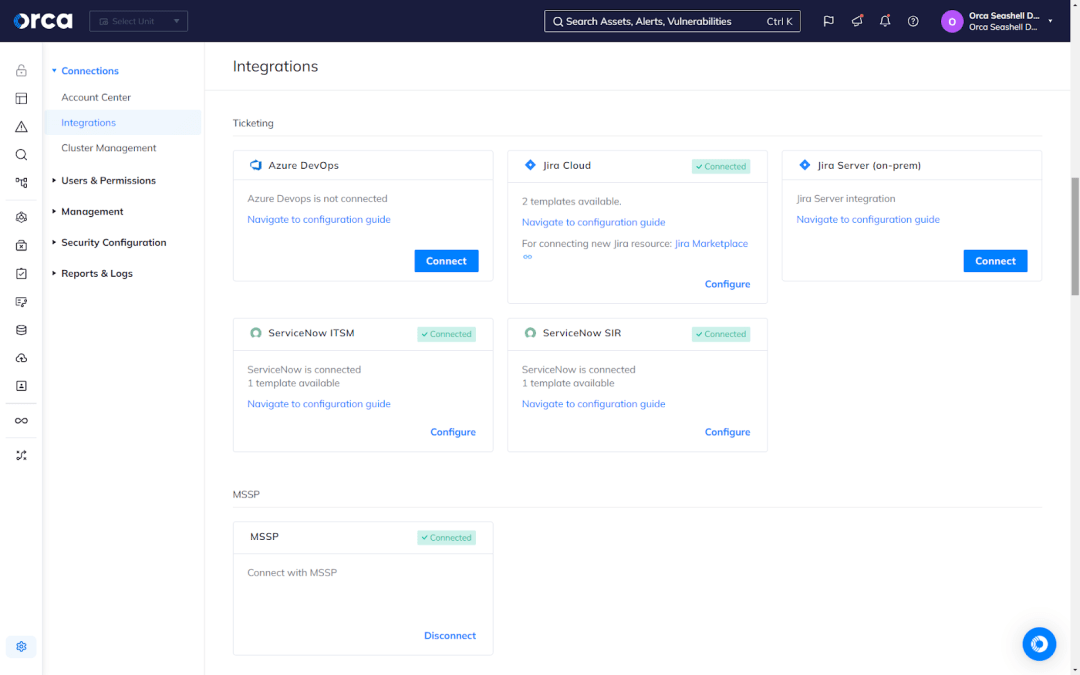
This explains why several cloud security vendors have started offering AI-SPM as part of their Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs). CNAPPs consolidate a number of essential cloud security solutions into one platform (such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP), Cloud Infrastructure and Entitlement Management (CIEM), Vulnerability Management, API Security, Shift Left Security, Kubernetes Security Posture Management, Container Security, etc.).
Despite the obvious benefits of adopting a CNAPP with AI-SPM capabilities, the results depend on the solution. That’s why organizations tend to favor a “true” Cloud Native Application Protection Platform—technology that features comprehensive capabilities built natively within the platform, rather than integrated after an acquisition or developed by a third party. Common complaints about non-native solutions include a disjointed user experience, alert fatigue from poorly connected point solutions, time-consuming deployments and configurations, blindspots in coverage, and more.
Why AI-SPM is important in cybersecurity
Current AI security challenges
Unlike other areas of cybersecurity, the challenges facing AI security practitioners are unique. For one, AI technologies face many of the same risks as other technologies in cloud computing, including vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, API risks, data risks, etc. But unlike other aspects of cloud computing, AI security also faces risks unique to the technology, as well as a shortage of seasoned experts, proven methods, and extensive and well-validated research.
This makes AI security a challenge arena for security professionals and a productive target for attackers. The unique conditions of AI security help contribute to the following challenges facing those in charge of securing the technology:
- Insecure default configurations: Currently, many AI services cater to developers and provide features that maximize speed and ease of use. This explains why the default configurations of AI resources often grant open access and excessive permissions. While this tendency may come as welcome news initially to developers, it produces security risks in a live environment that development, DevOps, and security teams must eventually address.
- Alert fatigue: The speed of AI development is exceptional, as developers can spin up and turn down AI resources with minimal effort. Combine this ease of use with the risk-inducing default configurations of AI resources, you get a formula that screams alert fatigue. This illustrates the importance of risk prioritization.
How AI-SPM addresses these challenges
AI-SPM helps solve the challenges presented in the previous section. The nascency of AI services and relative lack of solutions and proven methods make AI-SPM all the more important. The following details how AI-SPM addresses the unique challenges of AI security:
- Alert to and remediate insecure configurations: AI-SPM detects and alerts security teams to misconfigurations in deployed AI resources, including those generated via shadow AI practices. This ensures that AI resources do not experience prolonged risk exposure, and security teams can expedite the remediation of misconfigurations of critical and high severity. Additionally, AI-SPM solutions also allow organizations to address misconfigurations in the development phase, before resources get shipped to production. Commonly referred to as “shifting security left,” this practice maximizes efficiency for security, DevOps, and development teams by infusing security practices into the initial development phases.
- Prevent alert fatigue: Advanced AI-SPM solutions, including those offered as part of a true CNAPP, minimize alert fatigue through the dynamic assessment and prioritization of risks. These solutions automatically determine the severity of AI security risks and generate intelligible alerts that enable security teams to easily identify the most dangerous risks in their cloud estate. As a result, security teams can concentrate on the limited number of risks that demand their immediate attention, while delaying or ignoring the lower severity risks that would otherwise overwhelm them. Importantly, however, minimizing risk fatigue calls for AI-SPM solutions to accurately assess risk and also assign a severity score that differentiates the most time-sensitive critical risks from others deemed as critical.
Benefits of AI-SPM
AI-SPM solutions offer a number of benefits to organizations. While not an exhaustive list, they include the following:
- Greater visibility: AI-SPM solutions give security teams visibility into an area of cloud computing that they otherwise wouldn’t see and couldn’t control. These solutions identify deployed AI resources, including those connected to shadow AI activities, and how they exist in relation to other cloud assets and services. This insight allows security teams to understand what to protect and control.
- Enhanced threat detection and response: AI-SPM solutions detect and prioritize a comprehensive set of AI risks. This enables teams to accelerate their threat detection and response activities, as well as optimize their effectiveness in mitigating and remediating security threats. To facilitate the latter, some advanced AI-SPM solutions offer efficient and robust features for remediation efforts, including the use of GenAI.
- Continuous compliance: While most AI-SPM solutions support and enhance compliance efforts, the most advanced types allow organizations to sustain continuous compliance with regulatory frameworks and industry standards. This means organizations stay compliant with most of the security controls in their relevant framework(s), and actively work to resolve areas of non-compliance on a regular basis. Continuous compliance enables organizations to save time and anxiety associated with racing to prepare for an upcoming audit or dealing with the aftermath of failing one. Yet it calls for AI-SPM solutions that accelerate or automate compliance tasks, which often depend on features that offer automated workflows, out-of-the-box templates, auto-remediation options, and more.
Key features of an effective AI-SPM solution
Ability to detect AI packages
AI packages are used to train AI models to perform a specific task. These AI resources each contain numerous dependencies that are susceptible to vulnerabilities. This makes it especially important to detect= their existence in your cloud estate. That’s why you should look for AI-SPM solutions that can identify AI packages offered by a variety of vendors.
To illustrate, Orca detects more than 50 of the most commonly used AI packages to give you visibility into your AI and shadow AI, including Pytorch, TensorFlow, OpenAI, Hugging Face, scikit-learn, and many more.
Integration with CSP AI services
In order to promote AI security in cloud environments, AI-SPM solutions must natively integrate with the AI services offered by at least the major cloud service providers of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This remains essential to protecting the resources associated with Amazon Bedrock and SageMaker, Azure OpenAI, and Vertex AI.
AI best practices framework
Some of the advanced AI-SPM solutions offer AI best practices in the form of out-of-the-box frameworks. Using this type of framework, organizations can properly follow and monitor practices for managing and monitoring their AI network security, data protection, access controls, IAM, and more. These best practice frameworks also detect and alert security teams of misconfigurations.
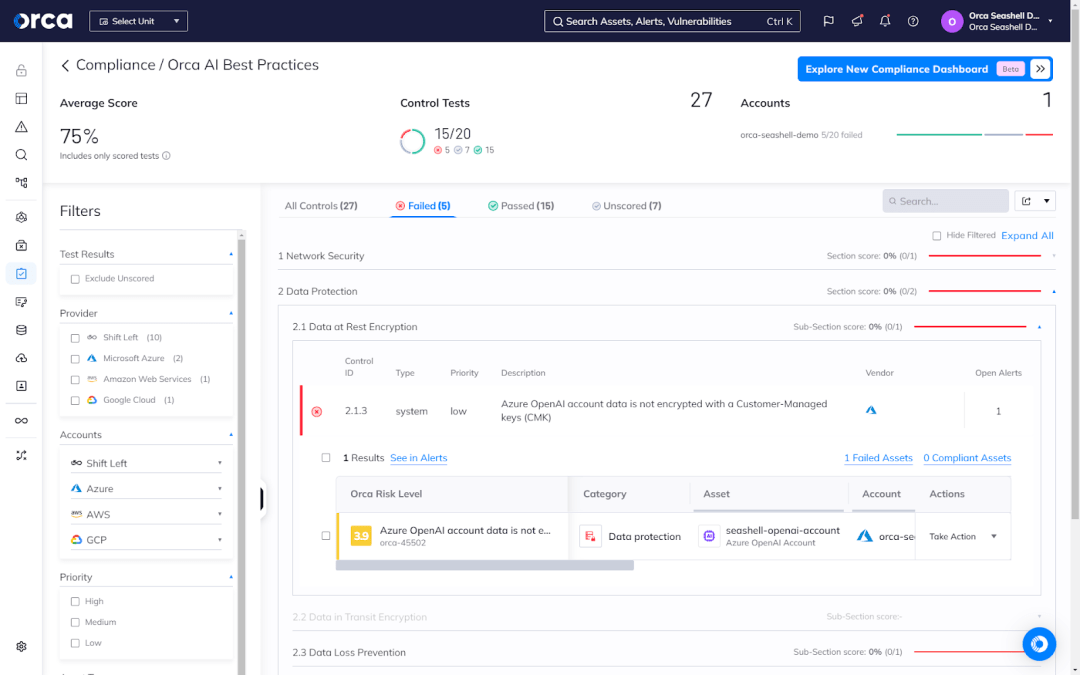
Sensitive data detection
AI resources contain multiple types of sensitive data, including data stored in AI projects as well as data used to train and fine-tune AI models. AI-SPM solutions need the ability to scan and classify this data, as well as alert security teams when training data contains personally identifiable information (PII). The latter is especially important, as models trained on sensitive data can subsequently leak the data to unauthorized parties. In membership inference attacks, for example, attackers manipulate training data to induce AI models into leaking sensitive information.
Third-party access detection
API keys committed to code repositories represent a significant security risk. Orca’s 2023 Honeypotting in the Cloud Report report found that attackers scan code repositories for access keys and can discover and use them in as little as 2 minutes. This illustrates the need for AI-SPM solutions that scan your code repositories and find the leakage of any AI access keys (e.g., tokens to Open AI, Hugging Face, or more). This ensures that you can prevent bad actors from gaining access to your AI models and their training data.
Unified platform and capabilities
Beyond deployment, look for solutions that natively integrate AI-SPM technology with other important security solutions in your stack. This includes the solutions you use for Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP), Cloud Infrastructure and Entitlement Management (CIEM), Vulnerability Management, Multi-Cloud Compliance, API Security, Data Security Posture Management, Container and Kubernetes Security, Cloud Detection and Response (CDR), Shift Left Security, and more. You should look for solutions that provide a unified interface, providing a single source of truth for risks and alerts. This enhances the speed and efficacy of your security operations.
Functional integrations
Look for AI-SPM solutions that offer deep technical integrations with popular applications used by development and DevOps teams. Both play a crucial role in ensuring the proper configuration of new AI assets as well as remediating existing risks found in the live environment. Favor solutions that don’t require developers to learn or use another application, as this eliminates the need for additional training, preserves productivity and efficiency, and reduces friction and developer frustration.
Challenges and considerations in implementing AI-SPM
Vendor reliability
It goes without saying the importance vendor reliability plays in cloud and AI security. Yet due to the nascency of AI services, you may find it more challenging to evaluate the effectiveness of a vendor’s AI-SPM solution.
One way of overcoming this challenge is to evaluate the vendor’s experience leveraging AI technologies safely and securely in their own platform. Consider whether the vendor leverages AI in the solutions they provide and how they secure their AI resources and innovation. For example, Orca became the first cloud security provider to leverage generative AI in its platform. Our commitment to AI security covers five core areas, including ensuring data integrity and privacy, securing AI pipelines, protecting AI keys, and more. Our approach to AI security leverages the same set of best practices and technology we provide to our clients.
Another way to evaluate vendor reliability is to consider their contributions to the AI security community. This can take the form of research or open-source projects. For example Orca has introduced AI Goat, the first open source AI security hands-on learning environment based on the OWASP Machine Learning Security Top Ten risks.
Cost and resource requirements
Like any business function, cost and resource requirements represent important considerations when choosing an AI-SPM solution. Many organizations find it challenging to adopt solutions that add another licensing fee to their existing security stack, require significant training and expertise, or diminish efficiency and productivity. This illustrates the importance of finding solutions that offer AI-SPM capabilities as part of a more comprehensive offering, such as true CNAPPs.
Additionally, evaluate the ease of use and intuitiveness of AI-SPM solutions before committing to a contract. Many AI-SPM vendors allow organizations to participate in a proof of concept (POC), allowing you to test drive the technology before making a commitment. When evaluating the solution, ensure the AI-SPM solutions don’t challenge the expertise or skills of your cloud security team.
Conclusion
Clearly, AI innovation is no longer a luxury for organizations, but a key requirement of maintaining their competitive advantage. AI development continues to accelerate at the speed of the cloud, with new services and innovations emerging everyday. It appears that the greatest challenges that will accompany AI are not our ability to innovate or develop, but secure and protect what we build.
Fortunately, AI security is rapidly maturing and continually bringing new solutions and capabilities online. Among today’s most exciting innovations, we find AI-SPM technology, which provides the ability to detect and remediate the AI security risks of today and tomorrow. While adopting an AI-SPM solution remains vital to your AI innovation, it also depends on the type of technology that you adopt. This guide helps support your decision-making in this area.
Learn more about the Orca Cloud Security Platform
The Orca Cloud Security Platform offers a true agentless-first CNAPP that identifies, prioritizes, and remediates security risks and compliance issues for AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Kubernetes, Alibaba Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
Orca’s solution offers comprehensive, end-to-end AI-SPM capabilities with Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP), Cloud Infrastructure and Entitlement (CIEM), API Security, Multi-Cloud Compliance, Vulnerability Management, Shift Left Security, and more.
Leveraging Orca’s patented SideScanning™ Technology, Orca contextualizes risks and recognizes when seemingly unrelated issues can create dangerous attack paths. This enables Orca to prioritize risks effectively, reduce alert fatigue, and ensure your teams can focus on the most critical and important tasks.
To see the Orca Platform in action, schedule a personalized demo with one of our experts.
FAQs
AI Security Posture Management is an emerging field of cloud security that involves addressing security risks and compliance issues associated with using AI models. It involves a collection of strategies, solutions, and practices designed to enable organizations to securely leverage AI models and LLMs in their business.
Like other cloud assets, AI models and LLMs present inherent security risks, including limited visibility, accidental public access, shadow data, unencrypted data, unsecured keys, and more.
In recent years, AI usage has increased dramatically. More than half of all organizations already use it in the course of their business. AI’s widespread adoption, coupled with the security risks of using AI services and packages, puts organizations at heightened risk of security incidents. The below figures help illustrate this risk:
- 94% of organizations using OpenAI have at least one account that is publicly accessible without restrictions.
- 97% of organizations using Amazon Sagemaker notebooks have at least one with direct internet access.
AI Security Posture Management involves several important activities to cover end-to-end AI risks, including:
- Cloud scanning and inventorying: The entire cloud estate is scanned to generate a full inventory of all AI models deployed within the cloud environment(s).
- Security posture management: Secure configuration of AI models is ensured, including network security, data protection, access controls, and IAM.
- Sensitive data detection: Sensitive information in AI models or training data is identified and alerts are generated so appropriate action can be taken.
- Third-party access detection: Teams are alerted when sensitive keys and tokens to AI services are exposed in code repositories.
The Orca Cloud Security Platform secures your AI models from end-to-end—from training and fine-tuning, to production deployment and inference.
- AI and ML Inventory and BOM: Get a complete view of all AI models that are deployed in your environment – both managed and unmanaged.
- Security posture management: Ensure that AI models are configured securely, including network security, data protection, access controls, and IAM.
- Sensitive data detection: Be alerted if any AI models or training data contain sensitive information so you can take appropriate action.
- Third-party access detection: Detect when keys and tokens to AI services— such as OpenAI, Hugging Face—are unsafely exposed in code repositories.






