According to the International Monetary Fund’s Global Financial Stability Report, extreme losses from cyber attacks have more than quadrupled since 2017 to $2.5 billion (USD). Among those affected, the IMF highlights financial institutions as especially susceptible, due to their control over sensitive information and other factors. The findings not only illustrate the importance of cloud security for these vulnerable institutions, but explain the motivation behind new regulations like the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
In this post, we dive deep into DORA compliance, revealing what the regulation entails, its importance, and best practices for meeting its requirements by January 17th, 2025.
What is DORA?
The European Union established the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) in January 2023 to strengthen the IT security of financial institutions as well as harmonize existing regulations across individual EU member states. The regulatory framework applies to all financial institutions operating in the EU. It also covers some third-party information and communication technology (ICT) vendors, including cloud service providers (CSPs).
DORA goes into effect on January 17th, 2025. That’s when designated authorities of each EU member state will begin enforcing the regulation. It is recommended that organizations begin preparing in advance to ensure that they’ll meet the requirements.
DORA’s five pillars of action
DORA consists of the following five core sections known as “pillars of action.”
Pillar #1: ICT risk management
Information and communication technology (ICT) risk management requires covered entities to develop, implement, and maintain a well-documented risk management framework. At the bare minimum, the framework should detail the strategies, policies, procedures, tools, and ICT protocols needed to adequately protect information and ICT assets. It must also present a full inventory of critical assets, functions, and ICT services, as well as their interdependencies.
Frameworks should detail how organizations plan to handle continuous risk assessments, risk identification and classification, and more. Additionally, they must include business continuity and disaster recovery plans for major events and incidents.
Pillar #2: Digital operational resilience testing
DORA requires covered entities to test their cybersecurity, identify any security risks like vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, and establish remediation plans. Organizations must perform these assessments and report on the results at least once a year, which the appropriate competent authorities will validate. Covered entities deemed critical to the financial system must meet additional measures, such as undergoing threat-led penetration testing (TLPT).
Pillar #3: ICT-related incidents
DORA establishes a dedicated reporting channel for ICT-related incidents, requiring all financial institutions to produce a root cause report within one month for major incidents. While organizations must report every incident to regulators, they may also need to notify customers and partners in more severe cases. Additionally, DORA requires organizations to implement systems for tracking, managing, and reporting ICT-related incidents and their severity.
Pillar #4: Information sharing
DORA encourages financial institutions to share information for the purposes of raising cybersecurity awareness. The compliance framework establishes standards for communicating information externally and internally, covering topics such as cyber threat intelligence, security solutions, and security strategies.
Still, organizations must comply with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) rules when sharing information with an external party.
Pillar #5: Third-party ICT risk management
DORA requires covered entities to implement a third-party risk program that aims to prevent disruptions to business continuity in the event of a supply chain attack or third-party breach. Covered entities must perform thorough due diligence of ICT providers, include special provisions in contracts, and identify and document any associated dependencies, among other stipulations.
What are the challenges of achieving DORA compliance in the cloud?
When factoring for cloud computing, compliance presents a number of challenges, regardless of the regulatory framework or industry benchmark. Those challenges are largely driven by the constant and rapid changes of cloud environments and the limitations of many cloud security and compliance solutions.
Below are a few of the major challenges that organizations encounter with cloud compliance and DORA:
- Visibility and monitoring: Many organizations struggle to gain and sustain full visibility of their cloud environments, preventing them from resolving their compliance issues. Agent-based cloud security solutions leave critical visibility gaps and often cover only 50% of cloud assets. Dedicated compliance solutions also offer limited visibility and lack the ability to detect all different types of risks, such as those associated with insecure APIs, sensitive data, AI models, and more.
- Risk prioritization: Many organizations suffer from alert fatigue in relation to compliance efforts. This often occurs from cloud security and compliance solutions that generate alerts for compliance issues, but fail to contextualize or prioritize them. As a result, security teams must sift through alerts and determine their severity, which slows response time, leads to missed critical risks, increases frustration and burnout, and more.
- Manual interventions: Legacy compliance tools are often not designed for cloud compliance, and as a result, they lack features that automate or accelerate critical tasks. This often results in manual interventions, workarounds, and duplicative tasks. Many modern cloud security alternatives share the same limitations, including point technologies and poorly integrated all-in-one platforms.
- Misalignment with tools and processes: For many organizations, compliance requires them to deviate from their everyday processes, workflows, and tools. The problem originates with cloud security solutions that lack technical integrations that complement established processes. This often leads to workflow inefficiencies, friction between teams, user frustration, and other consequences.
- Reporting: As covered previously, many cloud security and compliance solutions lack adequate visibility, monitoring, and functionality. This makes compliance reporting especially difficult for organizations, which must compensate for any technical deficiencies with manual interventions.
Best practices for achieving DORA compliance
To overcome the challenges of cloud compliance as it relates to DORA, organizations should embrace the following three practices.
1. Choose a DORA-compliant Cloud Service Provider
Vetting the partners in your supply chain is vital to achieving DORA compliance – and that includes your CSP partners.
While you won’t be able to validate if your CSP is DORA compliant until after January 2025, you can begin understanding how your CSP partners are preparing for the regulation’s imminent enactment. Many of the major CSPs—such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud—continue to publish guidance and updates related to DORA.
2. Choose the right cloud security solution
Choosing the right cloud security solution is a necessary step for achieving DORA compliance – for the challenges that we examined earlier. That’s why you should look for solutions that meet the following criteria:
- Complete coverage: Ensures full coverage of your cloud estate without blind spots, including multiple cloud environments. Coverage refers to visibility as well as the features and functionality available in the platform.
- Comprehensive: Protects against the different types of risks that may affect DORA compliance. This includes vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, malware, lateral movement, sensitive data risk, API risk, AI risk, identity and access risks, and more.
- Context-aware: Assesses risk using a holistic, unified approach. This means combining full coverage and comprehensive protection with a complete understanding of how cloud risks and assets interrelate and impact your business.
- Consumable: Makes it easy to consume the right insights at the right time, while also enhancing the speed, ease, efficiency, and convenience of critical tasks. An optimal user experience, integrations with popular applications used by your various teams, as well as AI-powered features all contribute in this regard. All of these features maximize productivity and alleviate the burden of compliance.
3. Embrace the model of continuous compliance
Organizations often approach compliance reactively, waiting for fast-approaching deadlines or audits before racing to fix issues and restore adherence with standards. This stop-and-start approach often makes compliance a significant operational and psychological burden. A far better and more sustainable approach is continuous compliance—the process of addressing compliance issues on an ongoing, regular basis.
Continuous compliance requires organizations to make compliance a key business priority, raise awareness about its importance, and leverage metrics and reporting for continuous improvement and visibility. Most importantly, it calls for sophisticated technology that makes the effort feasible without distracting from other obligations to business continuity.
Achieve DORA compliance with Orca
The Orca Cloud Security Platform is designed to help organizations in financial services and other sectors thrive in the cloud. The Orca Platform helps you identify, prioritize, and remediate security risks and compliance issues across all major CSPs, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, among others.
While not an exhaustive list, the Orca Platform offers the following features to help you continuously achieve DORA compliance:
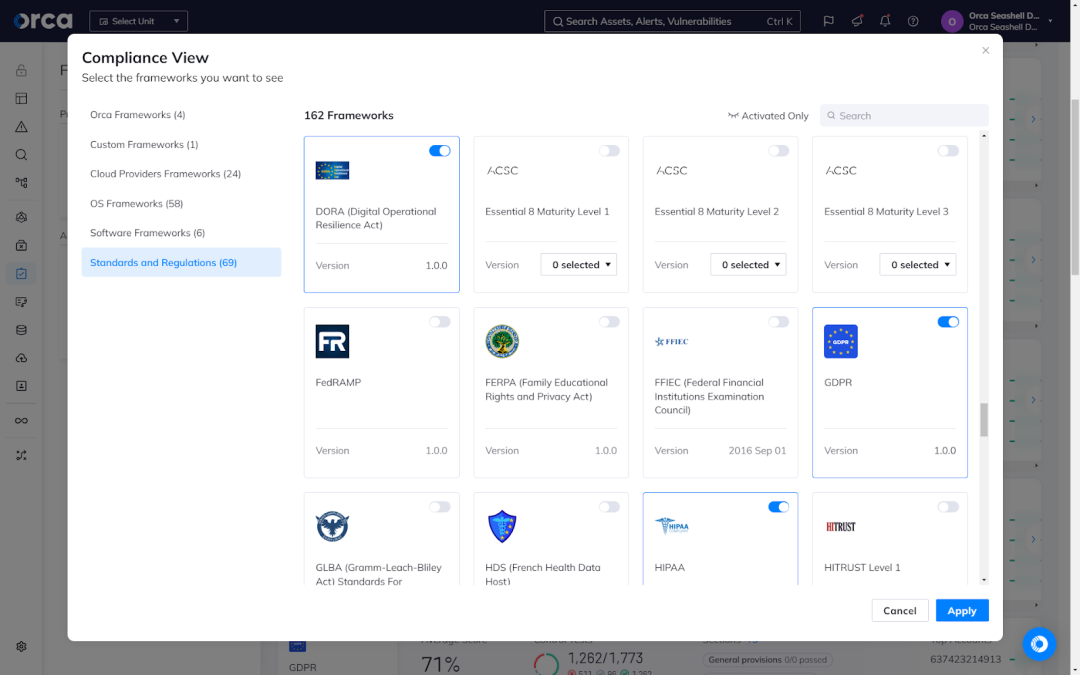
1. Out-of-the-box compliance frameworks
Orca offers more than 150 out-of-the-box compliance frameworks including DORA, GDPR, NIS Directive, NIS2 Directive, PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, CIS benchmarks, and more. Each framework includes a complete and up-to-date listing of security controls.
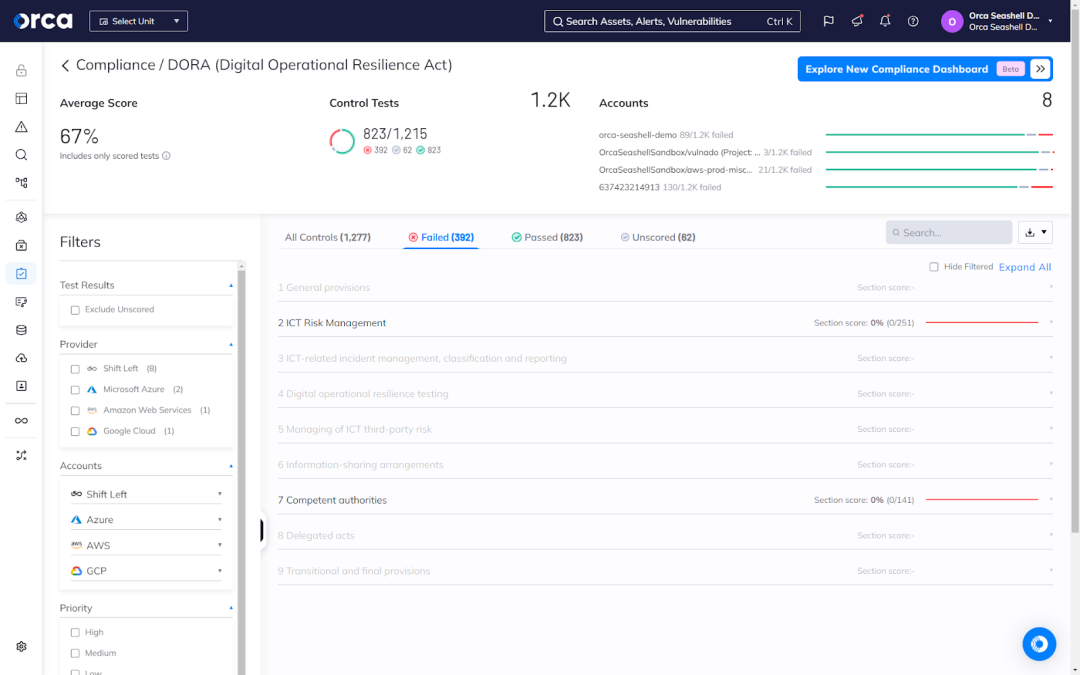
2. Automatic and continual compliance monitoring
Once you select the appropriate framework, Orca automatically assesses your current compliance status, which it continually updates to account for any new changes. In addition to your average compliance score, Orca also lists all security controls in the selected framework, including those that failed, passed, and those that require interventions outside the Orca Platform.
For each failed control, you can see the one or more risks forcing you out of compliance. You can also quickly access and address those alerts, which Orca prioritizes based on severity, using a full contextual awareness of your cloud estate.
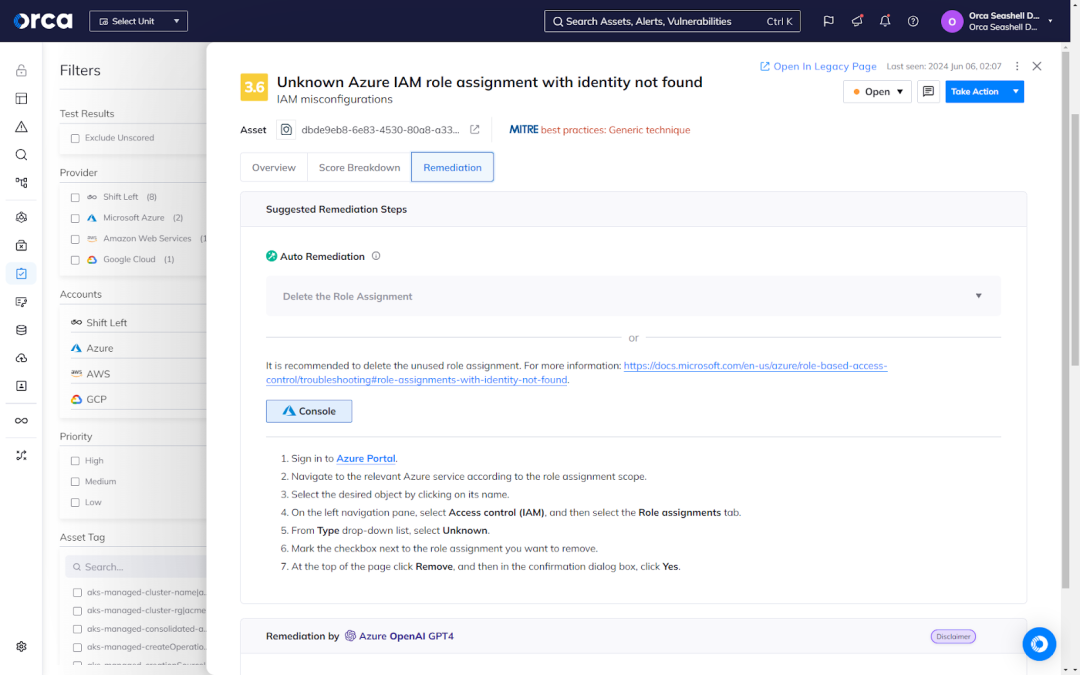
3. Automated and guided remediation
Orca offers automated and assisted remediation options to address compliance issues easily and efficiently. Auto-Remediation allows you to resolve risks with one click, while Orca’s manual remediation instructions provide actionable steps to resolve issues efficiently. Orca also offers an AI-powered remediation feature, which leverages GenAI to provide detailed remediation guidance and instructions tailored to your specific remediation process. This feature is available for multiple GenAI CSP services, including Azure OpenAI, Amazon Bedrock, and Google Vertex.
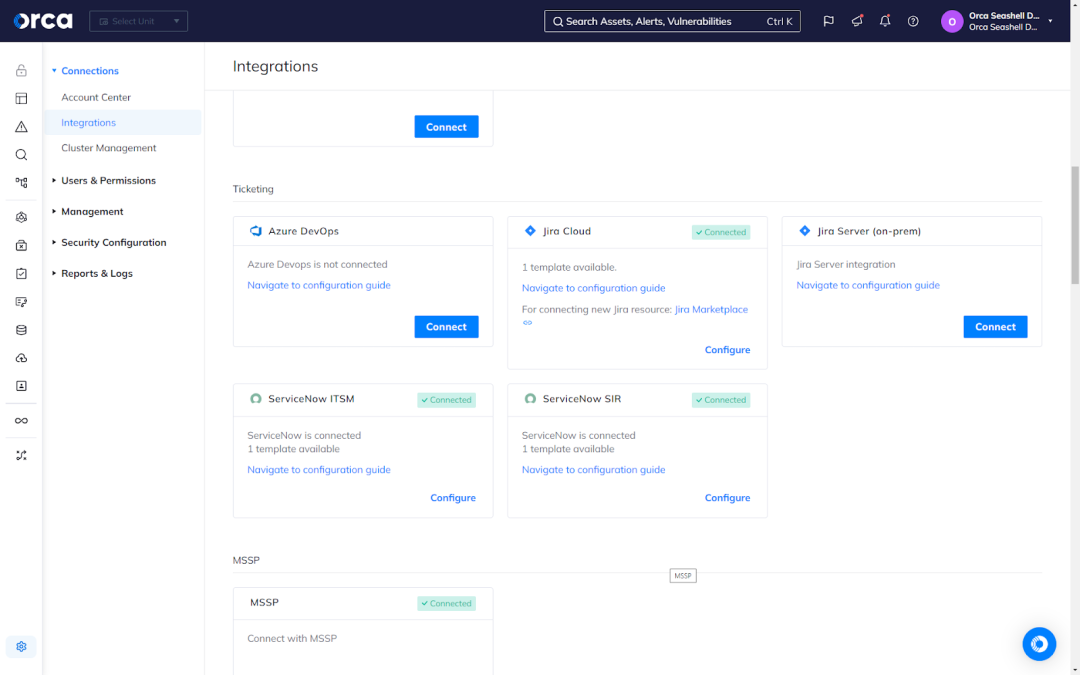
Orca also offers bidirectional integrations with popular ticketing solutions such as Jira and ServiceNow. This allows you to create a ticket for remediating an alert, assign it to the appropriate team member, and monitor and verify its status—all without leaving the Orca Platform.
4. Integrations and automation workflows
Speaking of technical integrations, Orca offers more than 50 – and they go beyond ticketing solutions. They include popular notification apps, security platforms, developer tools, and other solutions, allowing you to easily infuse intelligence from the Orca Platform into your existing workflows and applications. This translates into greater efficiency and productivity, as well as a harmonious partnership between security, development, and DevOps teams.
While Orca’s integrations are valuable on their own, the Orca Platform also offers automations to help you further boost productivity. Using automations, you can create automated workflows that trigger when custom conditions are met. For example, you can build workflows that automatically create and assign a ticket in Jira for specific alerts, or automatically auto remediate certain alerts based on risk type, severity, and other criteria.
When used for compliance, Orca’s automations can prove especially valuable. For example, they allow you to prioritize specific compliance issues automatically, allowing your team to concentrate on specific security controls and address them in a timely manner. In effect, they can help you move closer to achieving continuous compliance.
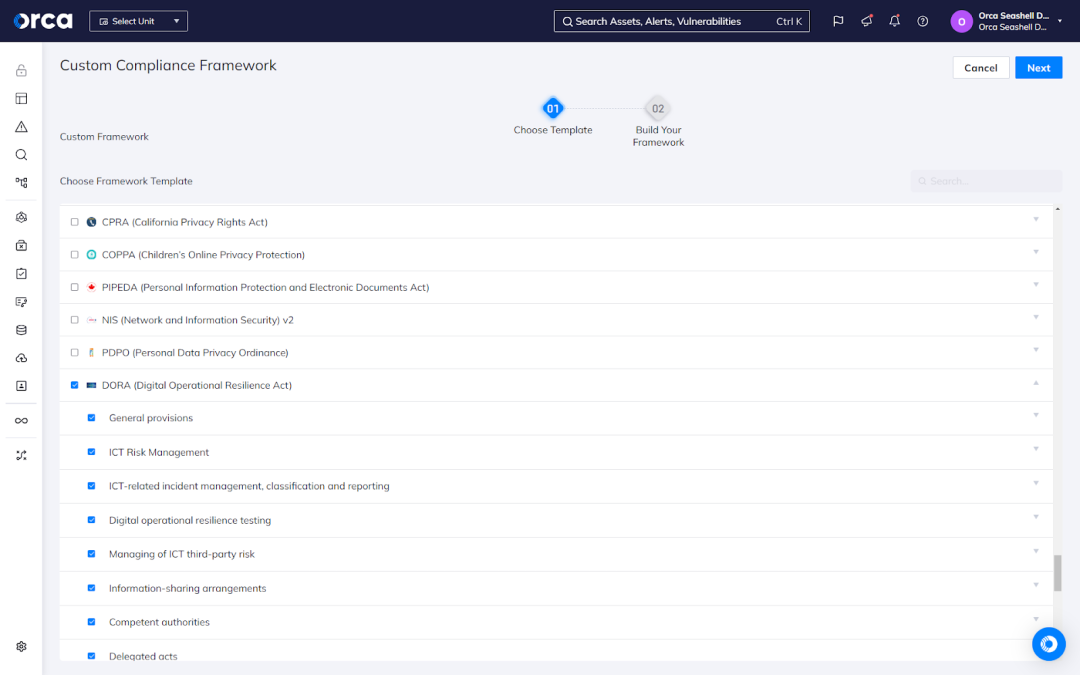
5. Customizable templates
More often than not, organizations must comply with more than one regulatory framework. To support your unique needs, Orca offers the ability to create custom frameworks. You can build a custom framework from scratch using Orca’s library of alerts, or combine two or more of Orca’s out-of-the-box templates. When using the template, Orca offers you the ability to combine entire frameworks or parts of frameworks, as well as add Orca alerts as appropriate.
Orca’s custom frameworks don’t impact your ability to leverage the Orca Platform’s full feature set or functionality. Instead, they give you the flexibility to ease your compliance efforts no matter the use case.
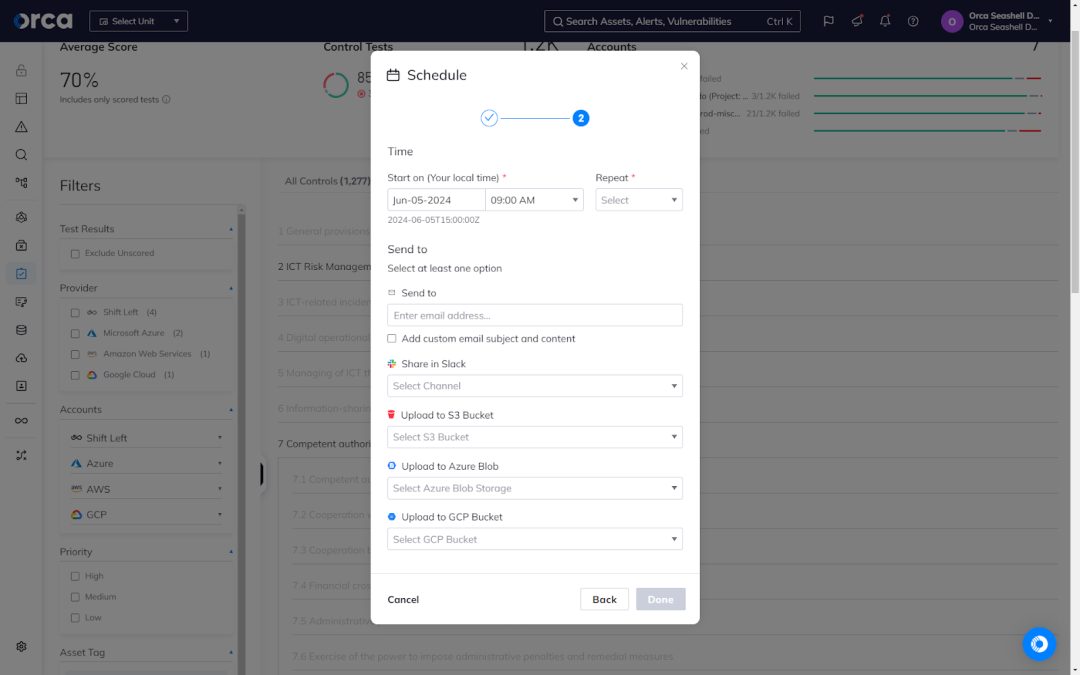
6. Flexible and automated reporting
While compliance reporting is often tedious and time-consuming, Orca eases the burden. For each compliance framework, Orca offers the option to automatically generate a compliance report in PDF, CSV, or JSON format, allowing you to share important information with the appropriate stakeholder(s). Additionally, you can also schedule reports to send automatically to an email address, Slack channel, storage bucket, or other location. You can also define the frequency, whether daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly.
Discover how Orca eases DORA compliance efforts
Offering more than 150 out-of-the-box frameworks and CIS® benchmarks, Orca empowers organizations to achieve continuous multi-cloud compliance efficiently and sustainably.
The Orca Cloud Security Platform is certified by the Center of Internet Security® (CIS®) Benchmarks across 24 cloud frameworks. This certification validates that the Orca Platform accurately identifies any configurations that deviate from recommended best practices in over 60 CIS® Benchmarks.
Ready to see how Orca can enhance your compliance efforts? Schedule a demo today.






